User Guide
HealthContact is a software for the receptionist of a family clinic who arranges telemedicine services between doctors and patients. It helps to keep track of patient data, patient appointments and patient bills for the family clinic.
Features
- Add a patient (addpatient, ap)
- Add an appointment of a patient (addappointment, aa)
- Add a bill of an appointment (addbill, ab)
- Edit a patient (editpatient, ea)
- Edit an appointment of a patient (editappointment, ea)
- Edit a bill of an appointment (editbill, eb)
- Find patient(s) (findpatient, fp)
- Find appointment(s) (findappointment, fa)
- Find bill(s) (findbill, fb)
- Sort patients (sortpatient, sop)
- Sort appointments (sortappointment, soa)
- Sort bills (sortbill, sob)
- Select a patient (selectpatient, slp)
- Select an appointment (selectappointment, sla)
- Set bill as paid (setpaid, sp)
- Set bill as unpaid (setunpaid, sup)
- List (list, ls)
- Delete a patient (deletepatient, dp)
- Delete a patient’s appointment (deleteappointment, da)
- Delete the bill of an appointment (deletebill, db)
- Undo (undo)
- Redo (redo)
- Clear (clear)
- Exit the program (exit)
- Help (help)
- Save the data
- Edit the data file
Others
Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java 11 or above installed in your Computer.
-
Download the latest HealthContact.jar from here.
-
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your HealthContact application.
-
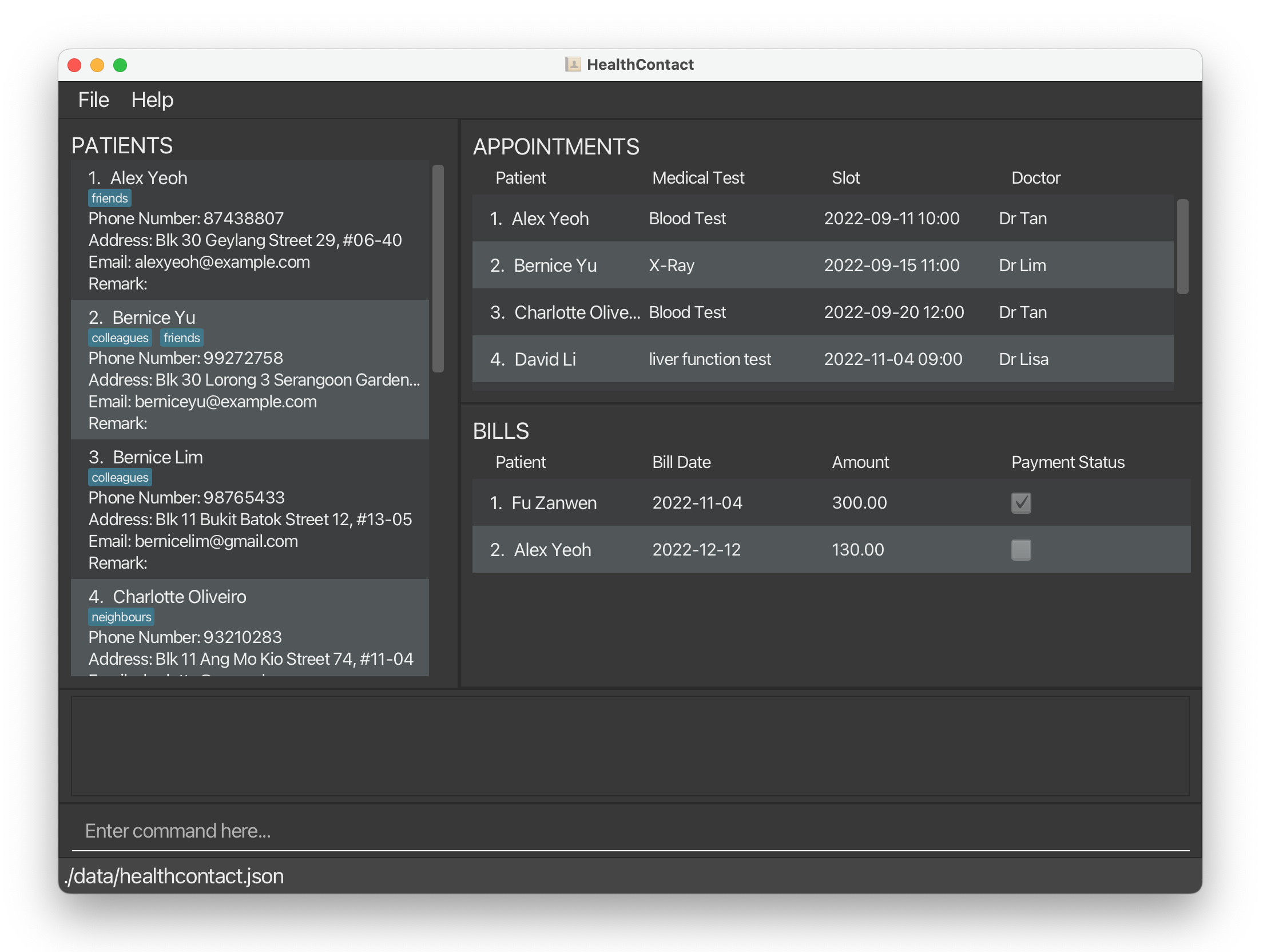
Double-click the file to start the app. The Graphical User Interface (GUI) similar to the one below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing help and pressing Enter will open the help window.
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
1. Features
1.1 Add
1.1.1 Add a patient addpatient, ap
Adds a patient to HealthContact with input information including name, phone number, email address, home address, remarks and tags.
Command word
addpatient or ap
Format
Command word <prefix><input> ...
-
Name must be different from existing patient and name is case-insensitive.
-
Remark and tags are optional.
-
A patient can be added with multiple tags.
-
The patient list, appointment list and bill list will show all data after adding.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
* |
n/ |
Name | 1. Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces 2. Must be different from existing patient’s name |
* |
p/ |
Phone number | Numbers with at least 3 digits |
* |
e/ |
Email address | local-part@domain |
* |
a/ |
Home address | Non-empty characters |
r/ |
Remark | Any characters | |
+ |
t/ |
Tag | One alphanumeric word |
Notes on symbols in first column:
* Must have (If they are duplicate prefixes, only the last one will be taken into account)
+ Can have multiple
Example:
ap n/Bernice Yu a/#11-330, blk 775, Bishan e/b.yu@nus.edu.sg p/80880011 t/NUS t/staffadds the patient.

1.1.2 Add an appointment of a patient addappointment, aa
Adds an appointment to HealthContact with input information including patient name, medical test, slot, and doctor.
Command word
addappointment or aa
Format
Command word <prefix><input> ...
-
Patient name input must strictly match the name of an existing patient, even the casing.
-
Slot must be in the format
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm, eg.2022-11-12 13:00. -
The input of four parameters must be different with the combination in other appointments.
-
Doctor and medical test are case-sensitive.
-
The input of four parameters must be different with the combination in other appointments, taking into consideration that doctor and medical test are case-sensitive, while patient name is case-insensitive.
-
The patient list, appointment list and bill list will show all data after adding.
-
The onus is on the user to check and ensure the following before adding an appointment:
- The appointment times for different patients with the same doctor do not clash with one another.
- The same patient/doctor does not have multiple appointments with times that clash with one another.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
* |
n/ |
Name | 1. Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces 2. must be existing patient’s name |
* |
s/ |
Slot | Valid date and time in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm |
* |
d/ |
Doctor name | Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces |
* |
t/ |
Medical test | Non-empty characters |
Notes on symbols in first column:
* Must have (If they are duplicate prefixes, only the last one will be taken into account)
+ Can have multiple
Examples:
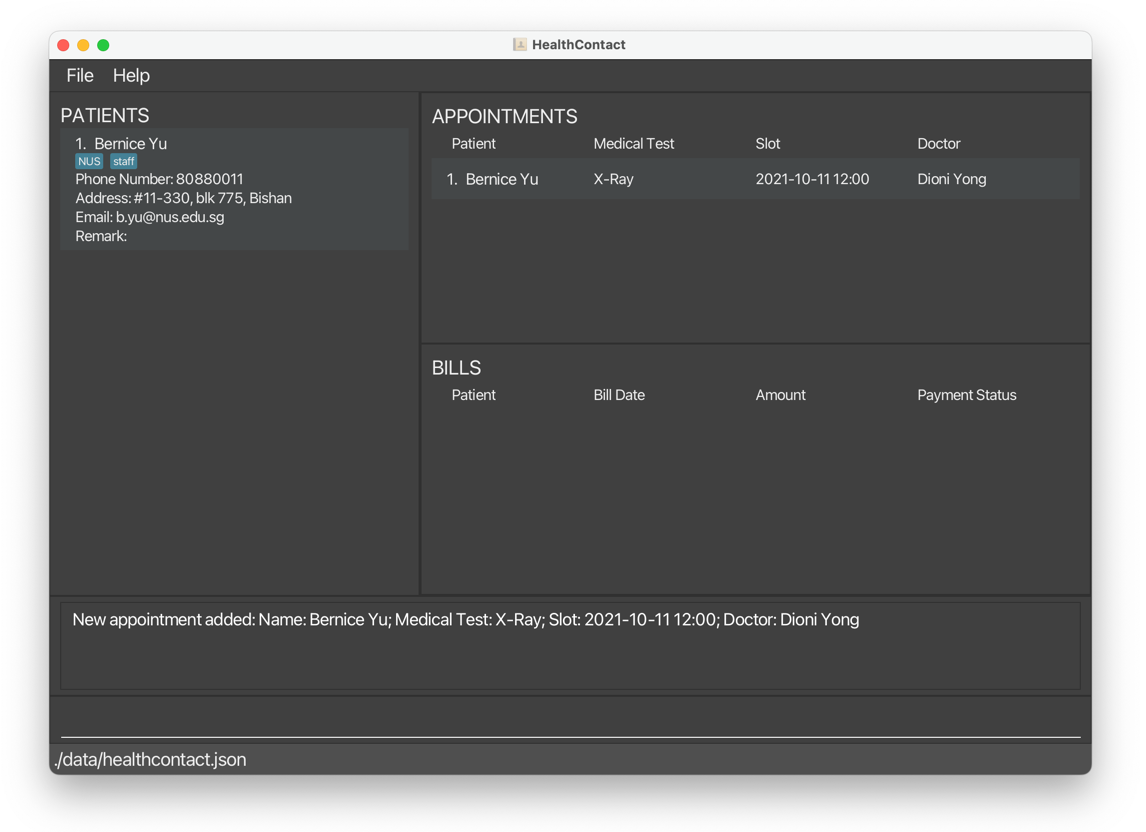
aa n/Bernice Yu s/2021-10-11 12:00 d/Dioni Yong t/X-Rayadds the appointment.
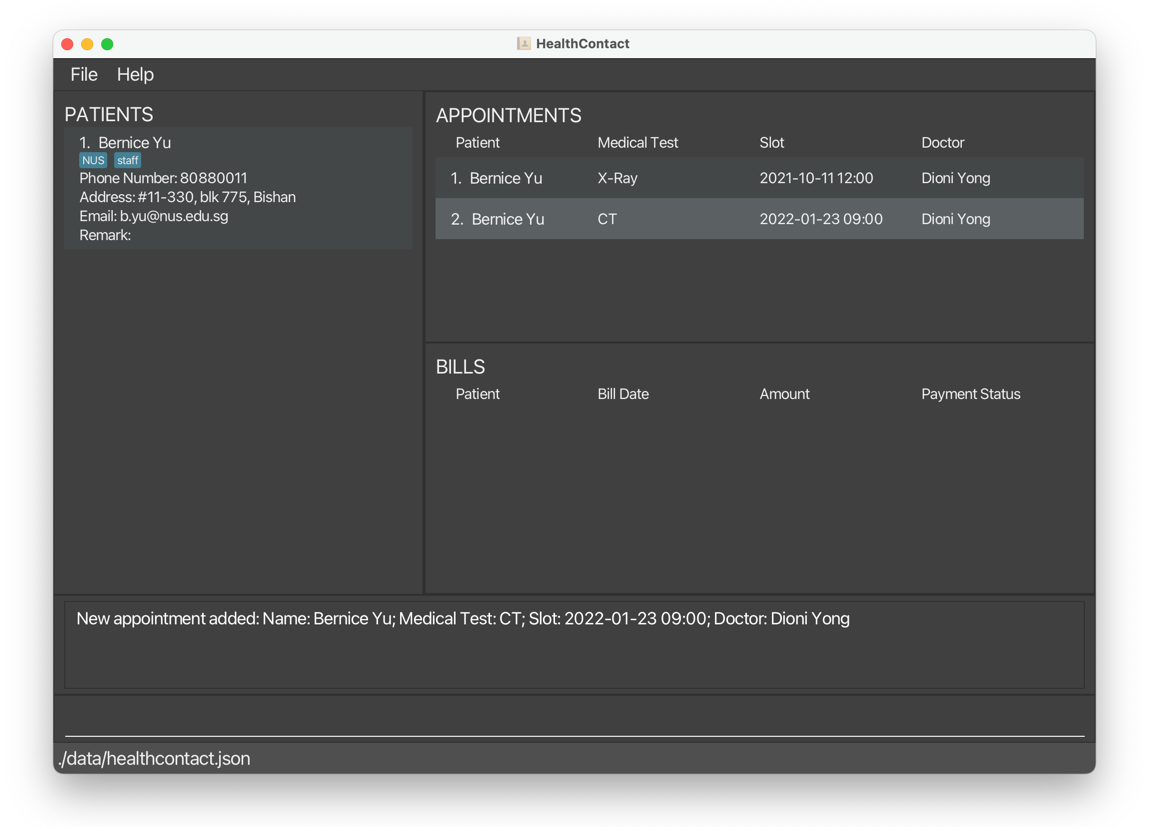
aa n/Bernice Yu s/2022-01-23 09:00 d/Dioni Yong t/CTadds another appointment forBernice Yu.
1.1.3 Add a bill of an appointment addbill, ab
Adds a bill attached to an appointment with input information including amount and bill date.
Command word
addbill or ab
Format
Command word <index of appointment> <prefix><input> ...
-
An amount must be positive number with at most 2 decimal places.
-
One appointment can be attached to no more than one bill.
-
A bill date must be in the format
yyyy-MM-dd, eg.2022-11-12. -
The patient list, appointment list and bill list will show all data after adding.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
** |
NA | Index of appointment | 1. Positive integer 2. Appears in the appointment list 3. The indicated appointment does not have bill |
* |
a/ |
Amount | Positive number with at most 2 decimal place |
* |
d/ |
Bill Date | Valid date in format yyyy-MM-dd |
Notes on symbols in first column:
** Must be directly after command word
* Must have (If they are duplicate prefixes, only the last one will be taken into account)
Example:
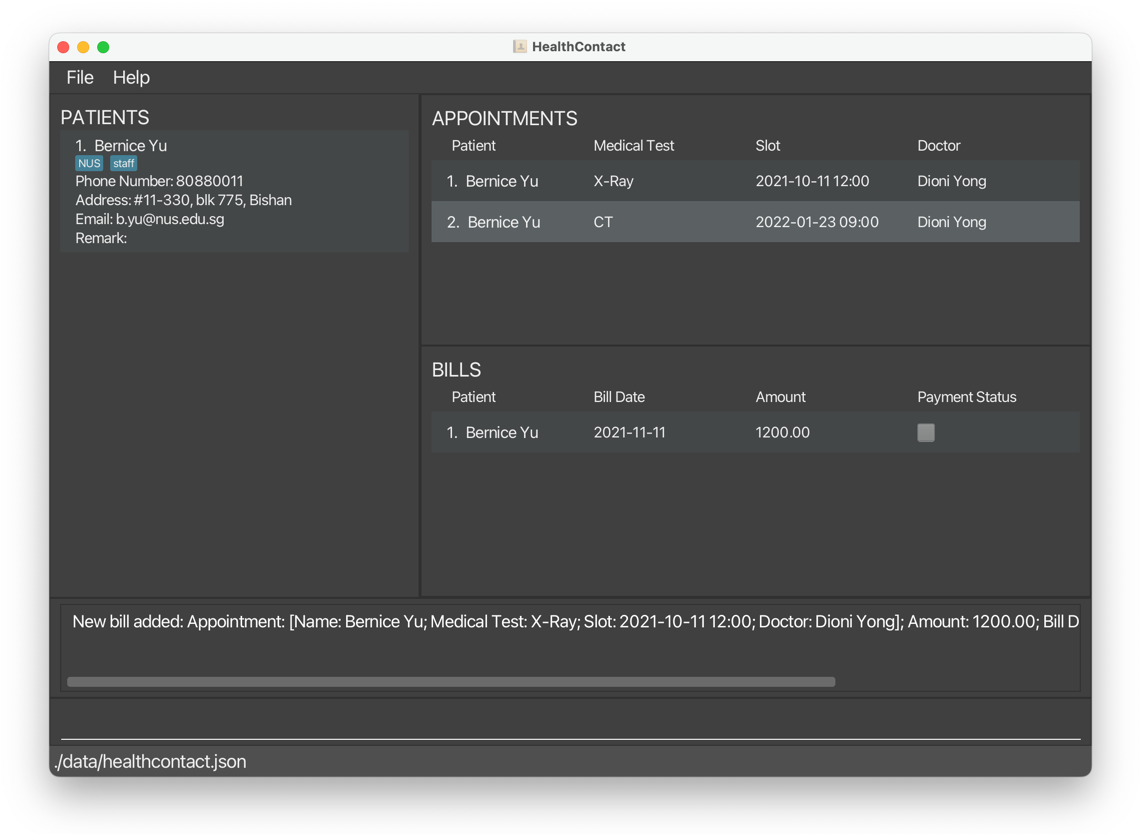
ab 1 a/1200.00 d/2021-11-11adds a bill to the first appointment in the displayed list.
1.2 Edit
1.2.1 Edit a patient editpatient, ep
Edits a patient’s information, such as name, phone number, address, email, remarks, and tags.
Command word:
editpatient or ep
Format:
Command word <index of patient> <prefix><input> ...
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
** |
NA | Index of patient | 1. Positive integer 2. Appears in the patient list |
* |
n/ |
Name | 1. Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces 2. Must not be existing patient’s name |
* |
p/ |
Phone | Numbers with at least 3 digits |
* |
e/ |
Email address | local-part@domain |
* |
a/ |
Home address | Non-empty characters |
r/ |
Remark | Any characters | |
+ |
t/ |
Tag | One alphanumeric word |
-
Edits the patient at the specified index. The index of patient refers to the index number shown in the displayed patient list.
The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
<input>refers to the new value of the field to be edited.- User input should be different from the previous information that the patient has.
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the person will be removed, i.e. adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the patient’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it. - The prefixes that can be used to edit patients can be found below in the parameter list.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
* |
n/ |
Name | 1. Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces 2. Must be different from existing patient’s name |
* |
p/ |
Phone number | Numbers with at least 3 digits |
* |
e/ |
Email address | local-part@domain |
* |
a/ |
Home address | Non-empty characters |
r/ |
Remark | Any characters | |
+ |
t/ |
Tag | One alphanumeric word |
Examples:
editpatient 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comedits the phone number and email address of the first patient on the displayed list to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively.
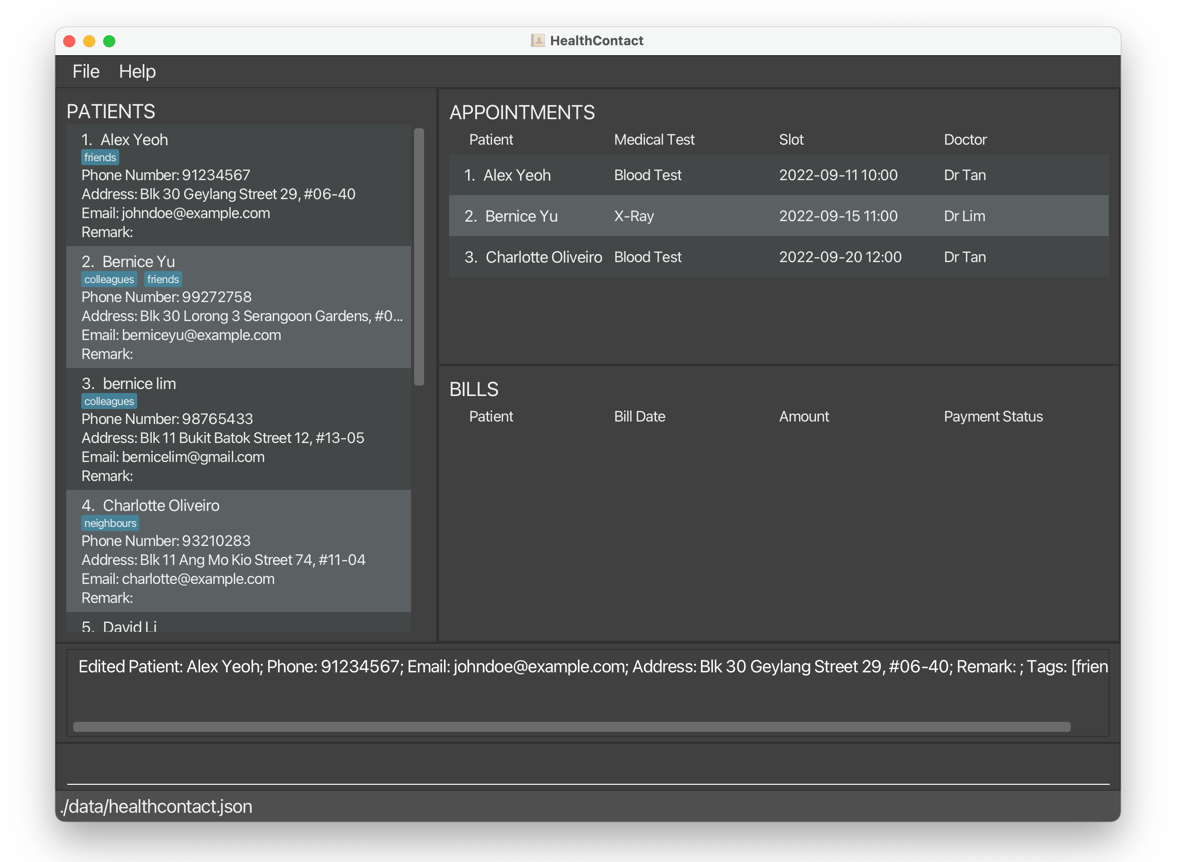
editpatient 2 n/Betsy Crower t/edits the name of the second patient on the displayed list to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
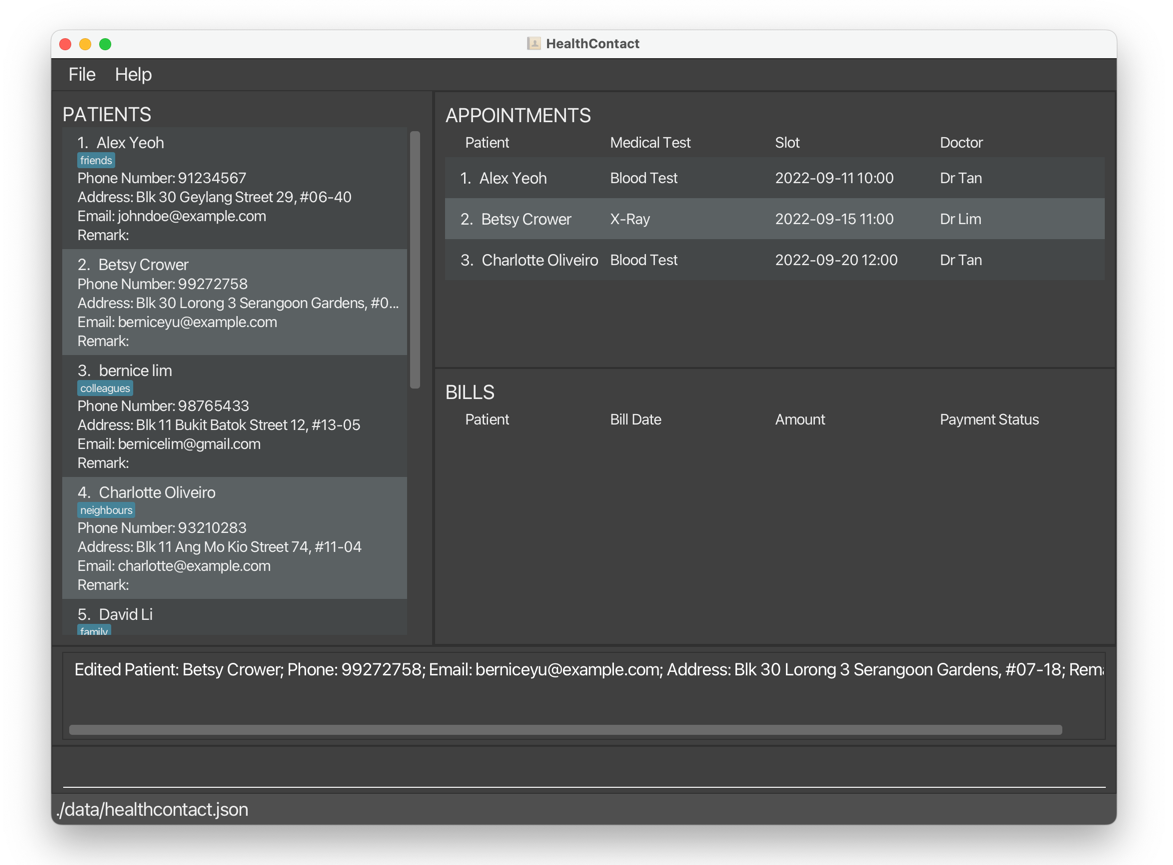
1.2.2 Edit an appointment of a patient editappointment, ea
Edits an appointment of a patient, such as name, medical test, slot, and doctor.
Command word:
editappointment or ea
Format:
Command word <index of appointment> <prefix><input> ...
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
** |
NA | Index of appointment | 1. Positive integer 2. Appears in the appointment list |
* |
n/ |
Name | 1. Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces 2. must be existing patient’s name |
* |
s/ |
Slot | Valid date and time in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm |
* |
d/ |
Doctor name | Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces |
* |
t/ |
Medical test | Non-empty characters |
-
Edits the appointment at the specified index. The index of appointment refers to the index number shown in the displayed appointment list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- The
<input>refers to the new value of the field to be edited. - User input should be different from the previous information that the appointment has.
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- The prefixes that can be used to edit patients can be found below in the parameter list.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
* |
n/ |
Name | 1. Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces 2. must be existing patient’s name |
* |
s/ |
Slot | Valid date and time in format yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm |
* |
d/ |
Doctor name | Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces |
* |
t/ |
Medical test | Non-empty characters |
Examples:
editappointment 1 n/David Li t/CT Scan s/2021-03-01 10:00 d/TanEdits the name, medical test, slot, and doctor of the 1st appointment to beDavid Li,CT Scan,2021-03-01 10:00, andTanrespectively.
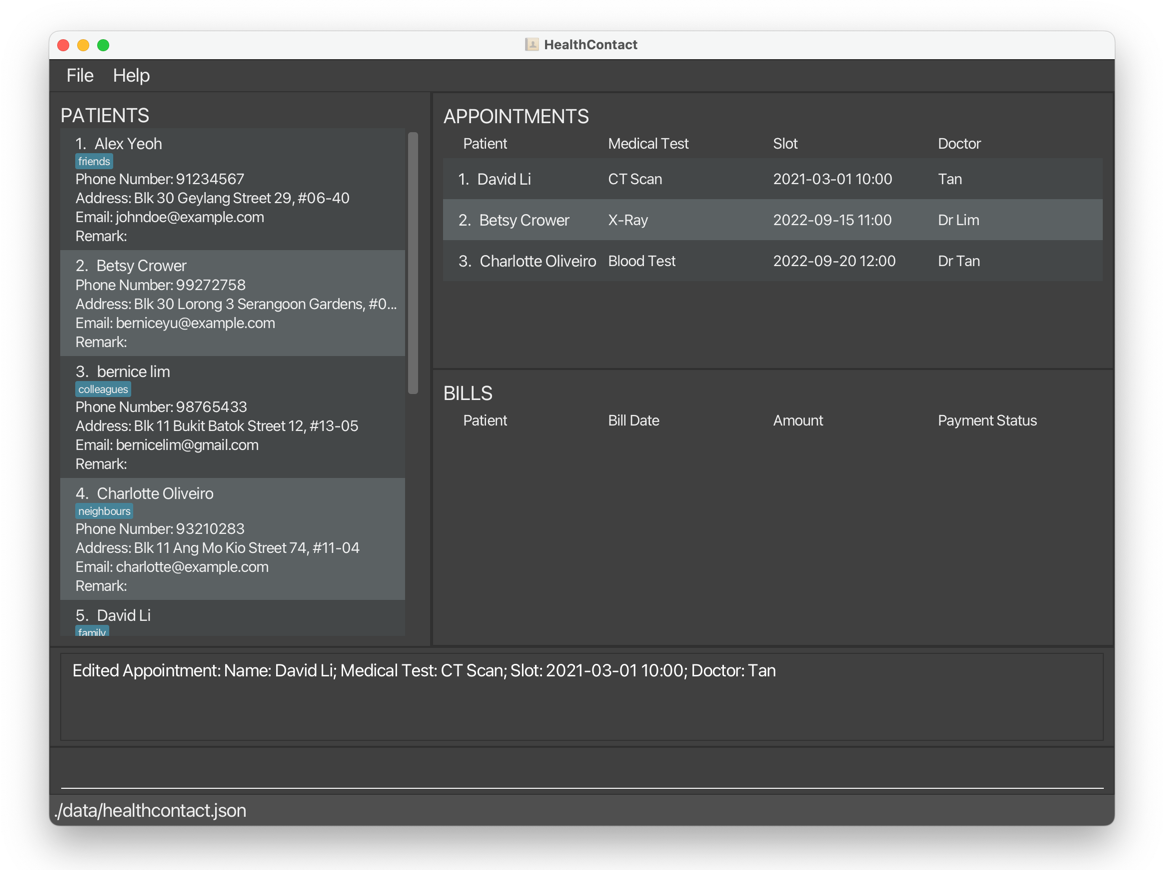
1.2.3 Edit a bill of an appointment editbill, eb
Edits the bill of an appointment.
Command word:
editbill or eb
Format:
Command word <index of bill> <prefix><input> ...
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
** |
NA | Index of bill | 1. Positive integer 2. Appears in the bill list |
* |
a/ |
Amount | Positive number with at most 2 decimal place |
* |
d/ |
Bill Date | Valid date in format yyyy-MM-dd |
-
Edits the bill at the specified index. The index of bill refers to the index number shown in the displayed bill list.
The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
Examples:
editbill 1 a/100edits the amount of the first bill to be100.
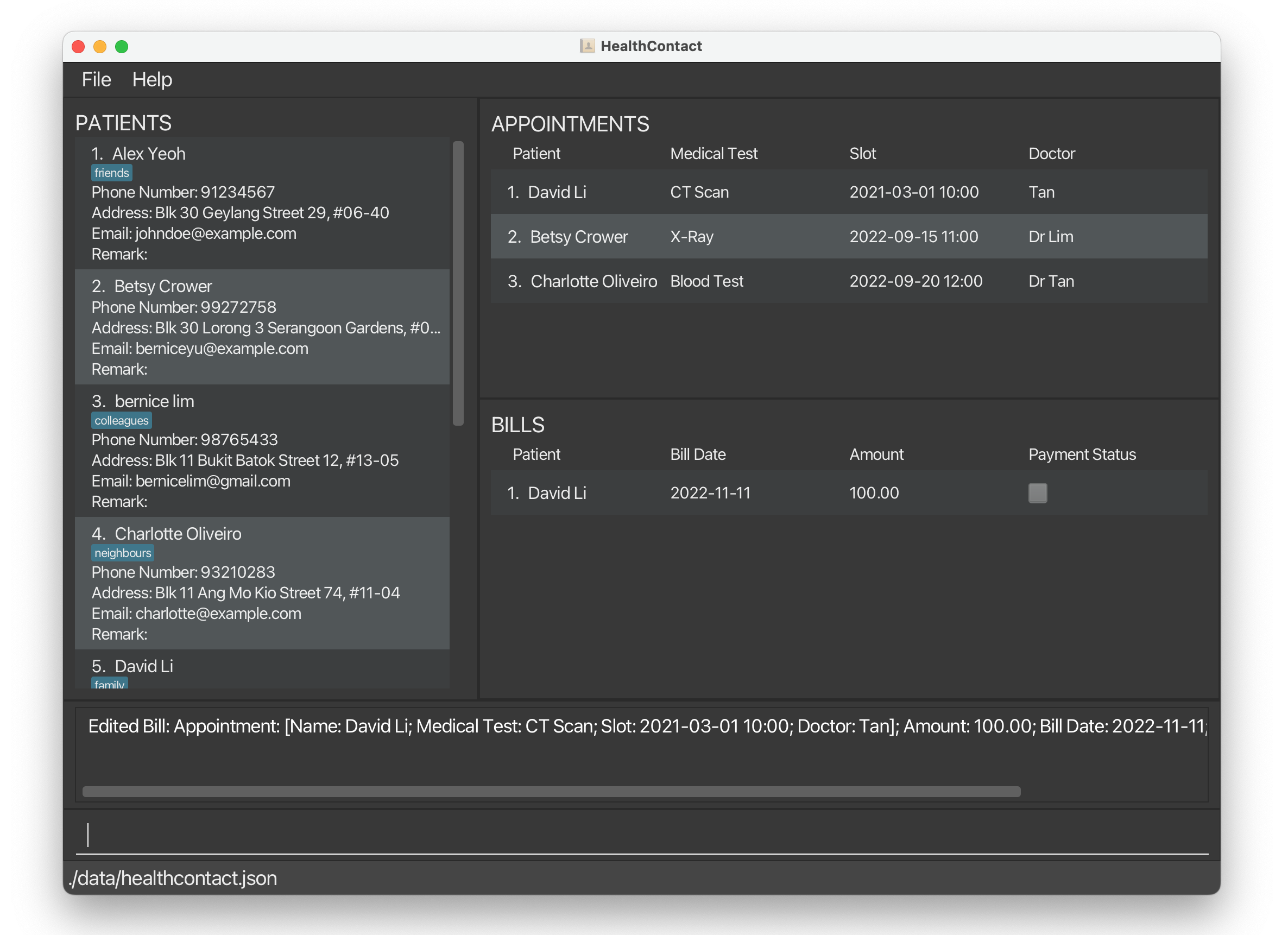
editbill 1 d/2022-10-10edits the bill date of the 1st bill to be2022-10-10.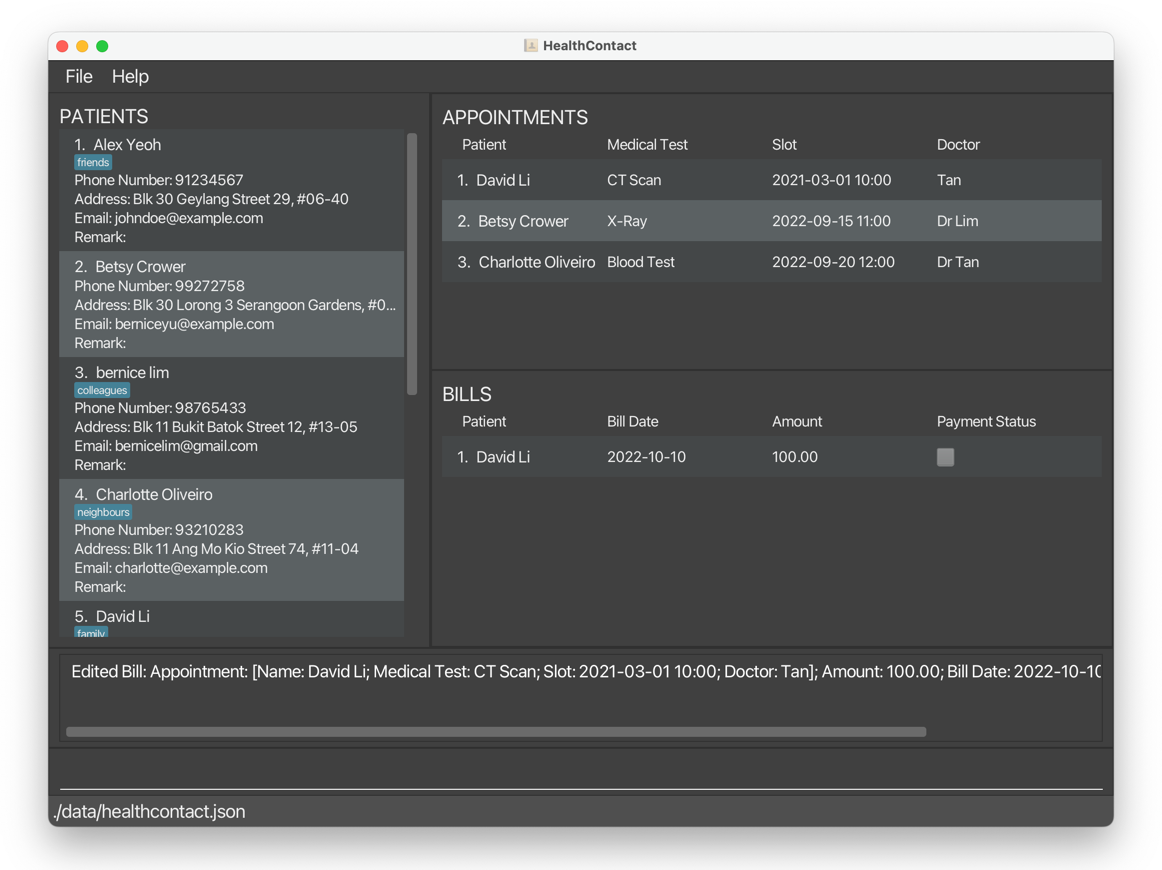
1.3 Find
1.3.1 Find patient(s) findpatient, fp
Filters patients by one or more fields using their prefixes, and their corresponding inputs (numbers, letters, special characters). The filtered patients are then listed as an indexed list.
Command word:
findpatient or fp
Format:
Command word <prefix><input> ...
- The command words are
findpatientorfp. - The prefixes that can be used are provided in the parameter list below.
- The filter is case-insensitive, e.g. han will match Han.
- The user can filter using full words or partial words, e.g. han will match Hannah.
- The user can only filter according to the input constraints of each field as shown in the parameter list below.
- The user can filter using one field or multiple fields at once, but each field can only be used once in a single command(except tags).
- If there are no prefixes keyed in, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the input after a prefix is empty/invalid, an error message with the constraint of the field will be shown.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint |
|---|---|---|
n/ |
Name | Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces |
p/ |
Phone number | A number consisting of one or more digits, and spaces before and/or after the number are allowed |
e/ |
Email address | Non-empty characters |
a/ |
Home address | Non-empty characters |
r/ |
Remark | Non-empty characters |
t/ |
Tag | One alphanumeric word, and spaces before and/or after the number are allowed |
Examples:
findpatient n/alexreturnsAlex Yeohandalex tan.
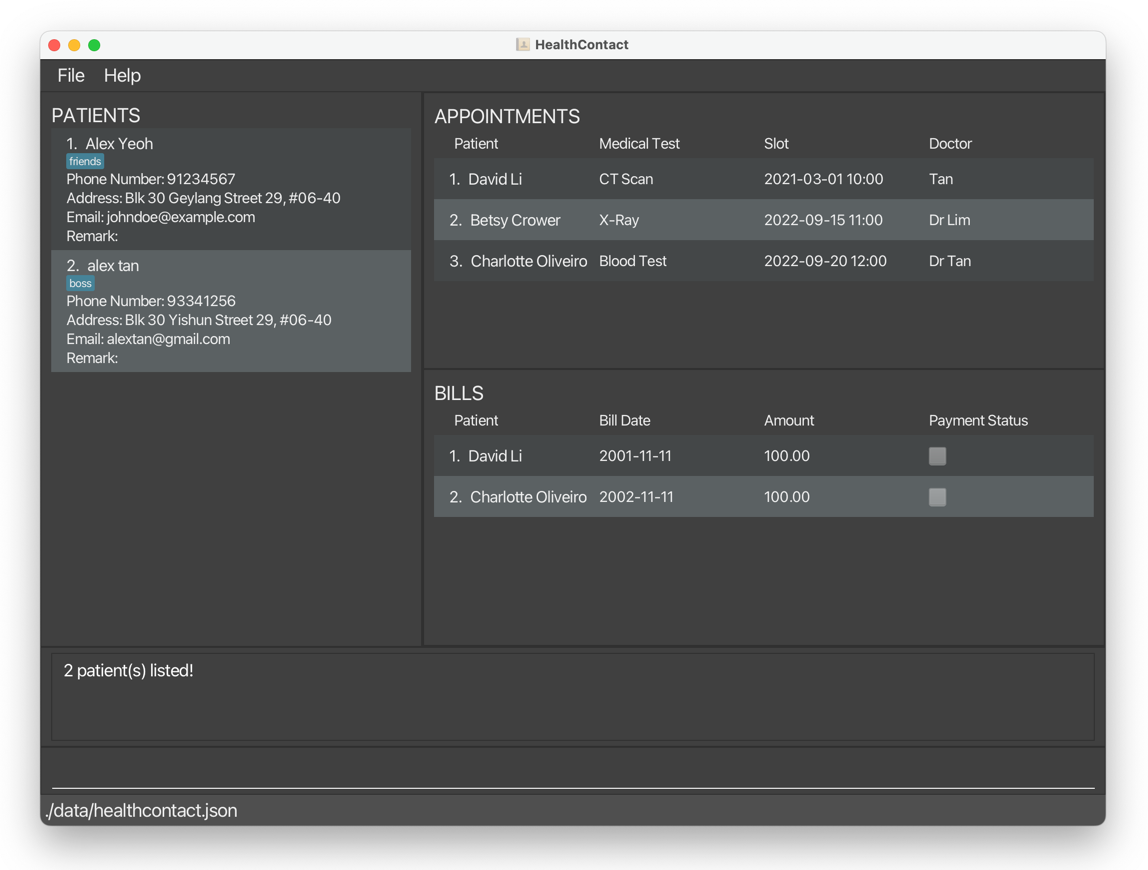
fp t/friends t/colleagues n/bernicereturns onlyBernice Yuwith the tagsfriendsandcolleagues.
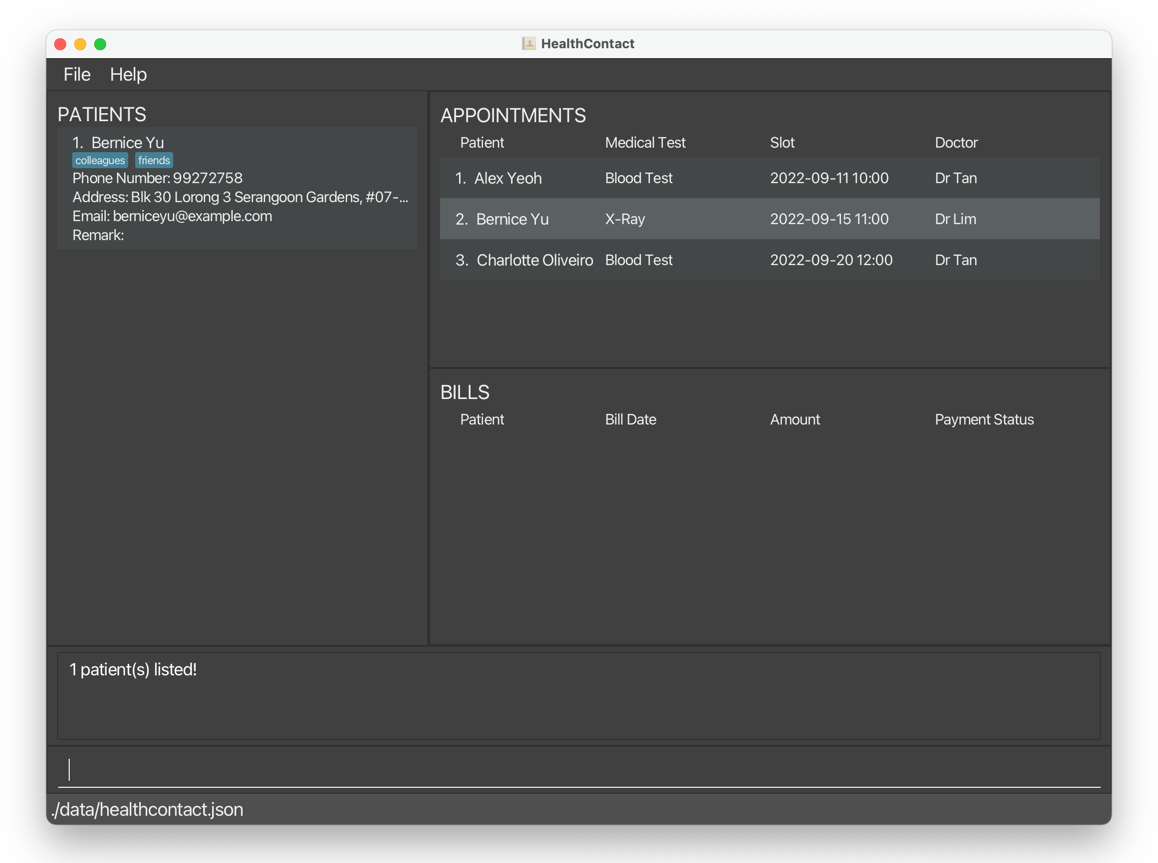
1.3.2 Find appointment(s) findappointment, fa
Filters appointments by one or more fields using their prefixes, and their corresponding inputs (numbers, letters, special characters).
Command word:
findappointment or fa
Format:
Command word <prefix><input> ...
- The command words are
findappointmentorfa. - The prefixes that can be used are listed in the parameter list below.
- The filter is case-insensitive, e.g. han will match Han.
- The user can filter using full words or partial words, e.g. han will match Hannah.
- The user can only filter according to the input constraints of each field as shown in the parameter list below.
- The user can filter using one field or multiple fields at once, but each field can only be used once in a single command.
- If there are no prefixes keyed in, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the input after a prefix is empty/invalid, an error message with the constraint of the field will be shown.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint |
|---|---|---|
n/ |
Name | Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces |
t/ |
Medical Test | Non-empty characters |
s/ |
Slot | Only numbers, “-“, “:” and spaces |
d/ |
Doctor | Only alphanumeric characters and spaces |
Examples:
findappointment t/x-rayreturnsBernice Yu’s appointment with medical testX-ray.
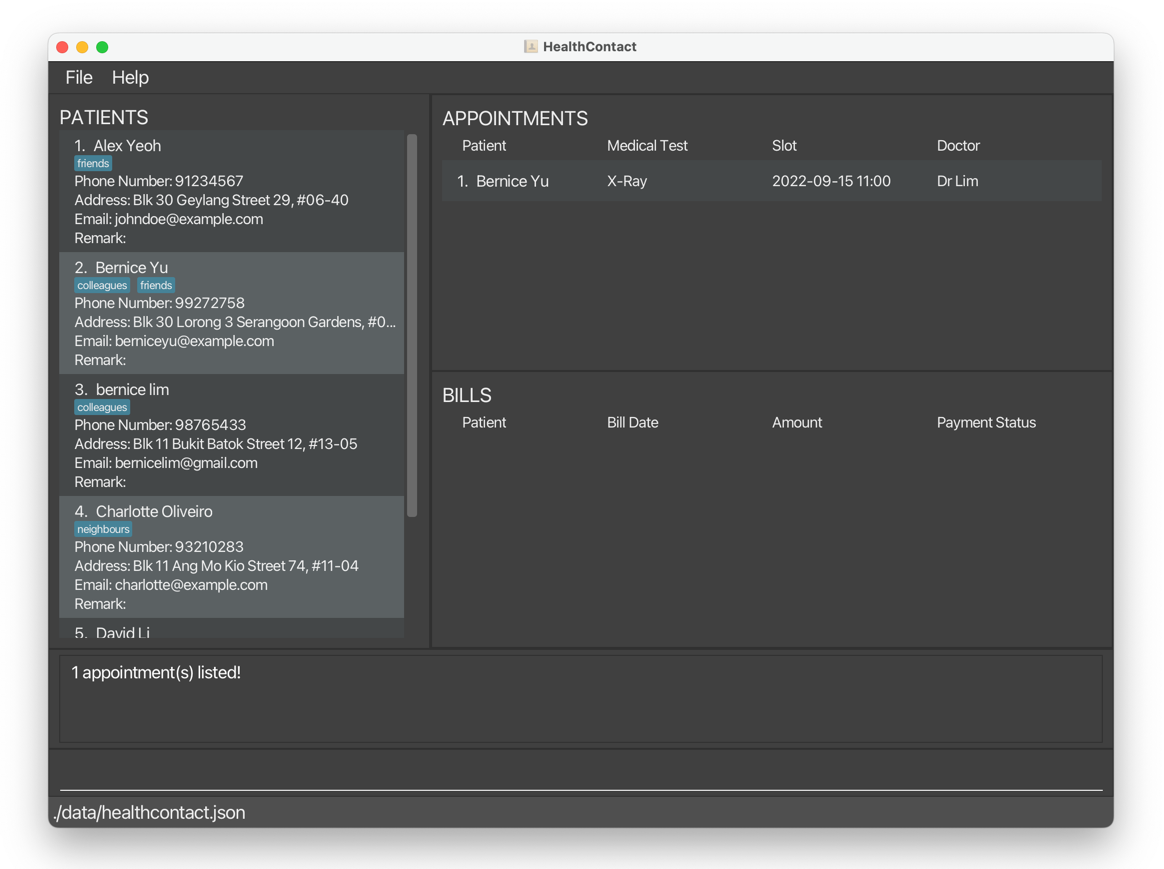
fa d/Dr Tan n/Alexreturns onlyAlex Yeoh’s appointment withDr Tan.
1.3.3 Find bill(s) findbill, fb
Filters bills by one or more fields using their prefixes, and their corresponding inputs (numbers, letters, special characters).
Command word:
findbill or fb
Format:
Command word <prefix><input> ...
- The command words are
findbillorfb. - The prefixes that can be used are listed in the parameter list below.
- The filter is case-insensitive, e.g. han will match Han.
- The user Can filter using full words or partial words, e.g. han will match Hannah.
- The user can only filter according to the input constraints of each field as shown in the parameter list below.
- The user can filter using one field or multiple fields at once, but each field can only be used once in a single command.
- If there are no prefixes keyed in, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the input after a prefix is empty/invalid, an error message with the constraint of the field will be shown.
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint |
|---|---|---|
n/ |
Name | Non-empty alphanumeric characters and spaces |
d/ |
Bill date | Only numbers, “-“ and spaces are allowed |
a/ |
Amount | Positive number with at most two decimal places, and spaces before and/or after the number are allowed |
p/ |
Payment Status | Only “paid” or “unpaid” in any case |
Examples:
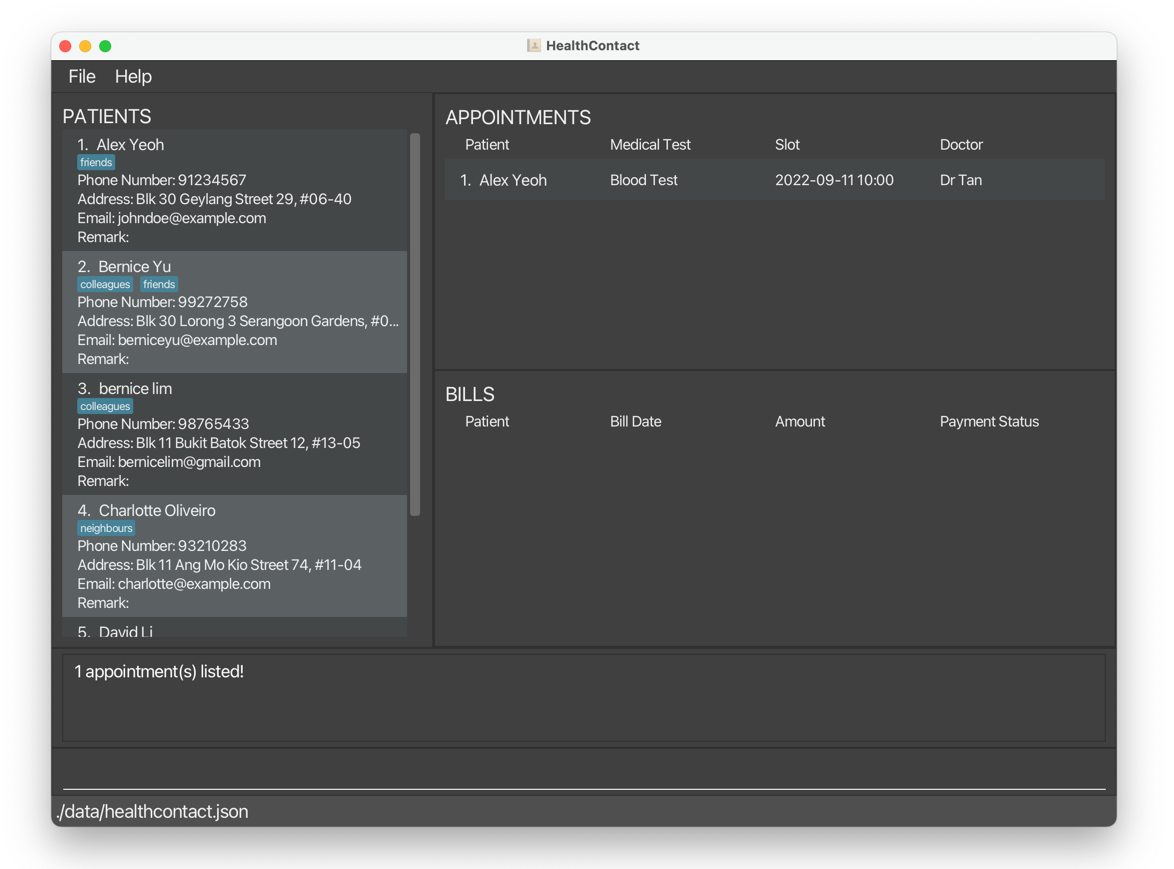
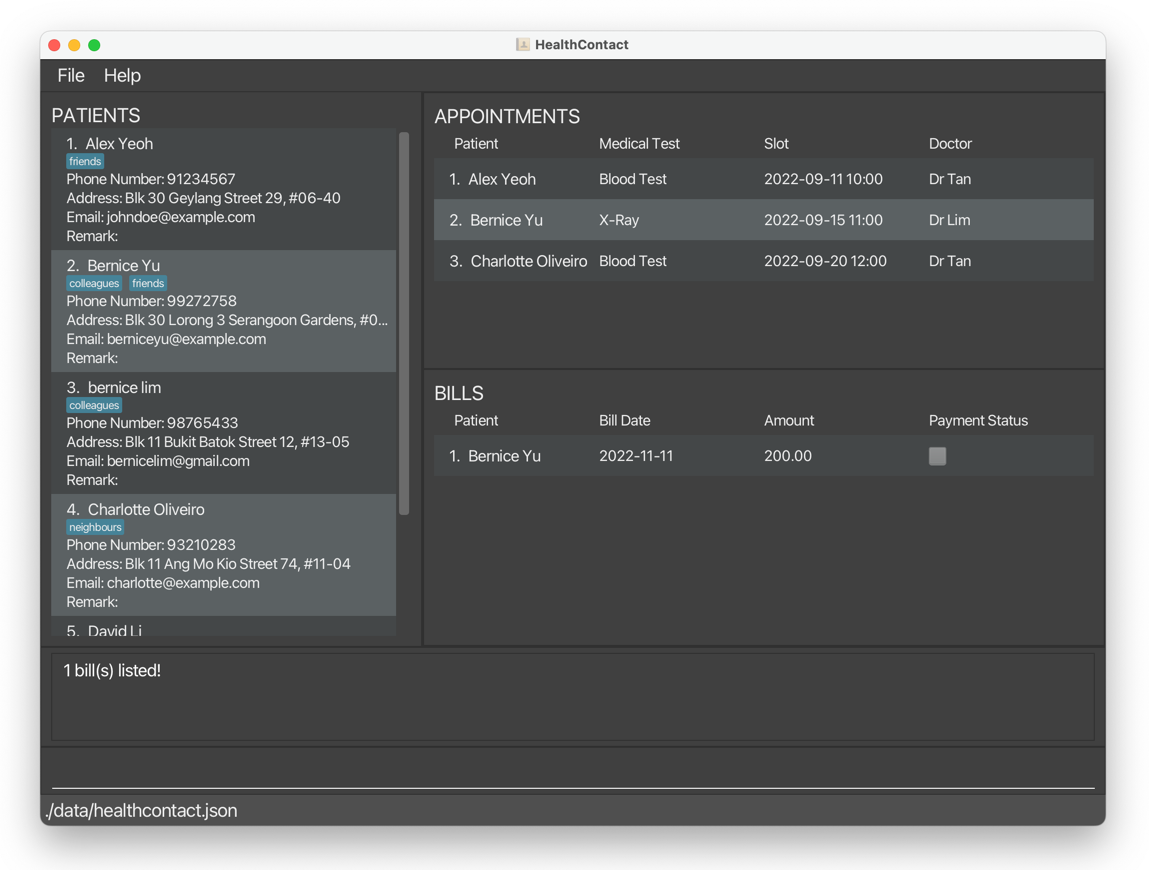
findbill n/Ber p/unpaid returns Bernice Yu’s unpaid bill
1.4 Sort
1.4.1 Sort patients sortpatient, sop
Sorts patients by a single field.
Command word:
sortpatient or sop
Format:
Command word c/<input> o/<input>
- The command word is
sortpatientorsop. - The prefixes are
c/for Criteria ando/for Order. - The criteria can be Name of patient (
name), Phone number of patient (phone), Email address of patient (email), Address of patient (address). - The order can be Ascending (
asc) or Descending (desc). - If there are no prefixes keyed in, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the input after a prefix is empty/invalid, an error message with the constraint of the field will be shown.
Examples:
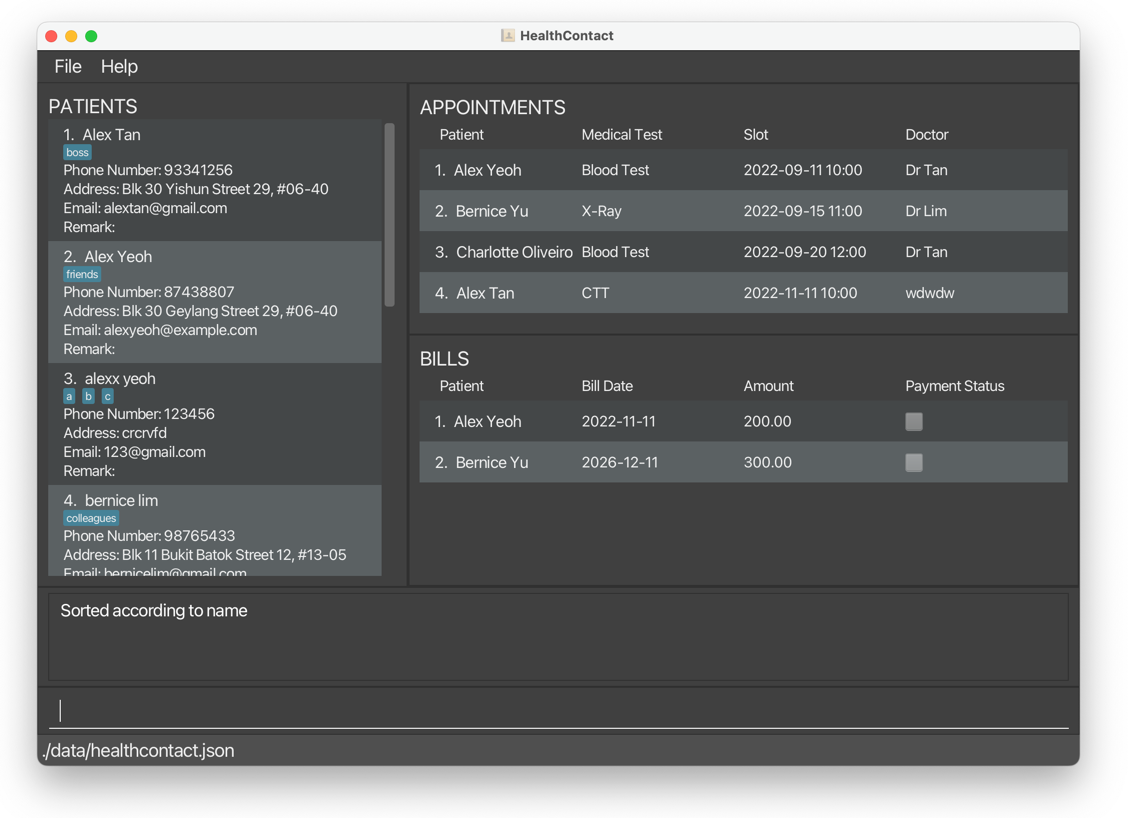
sortpatient c/name o/ascreturns patients sorted by name in ascending order.
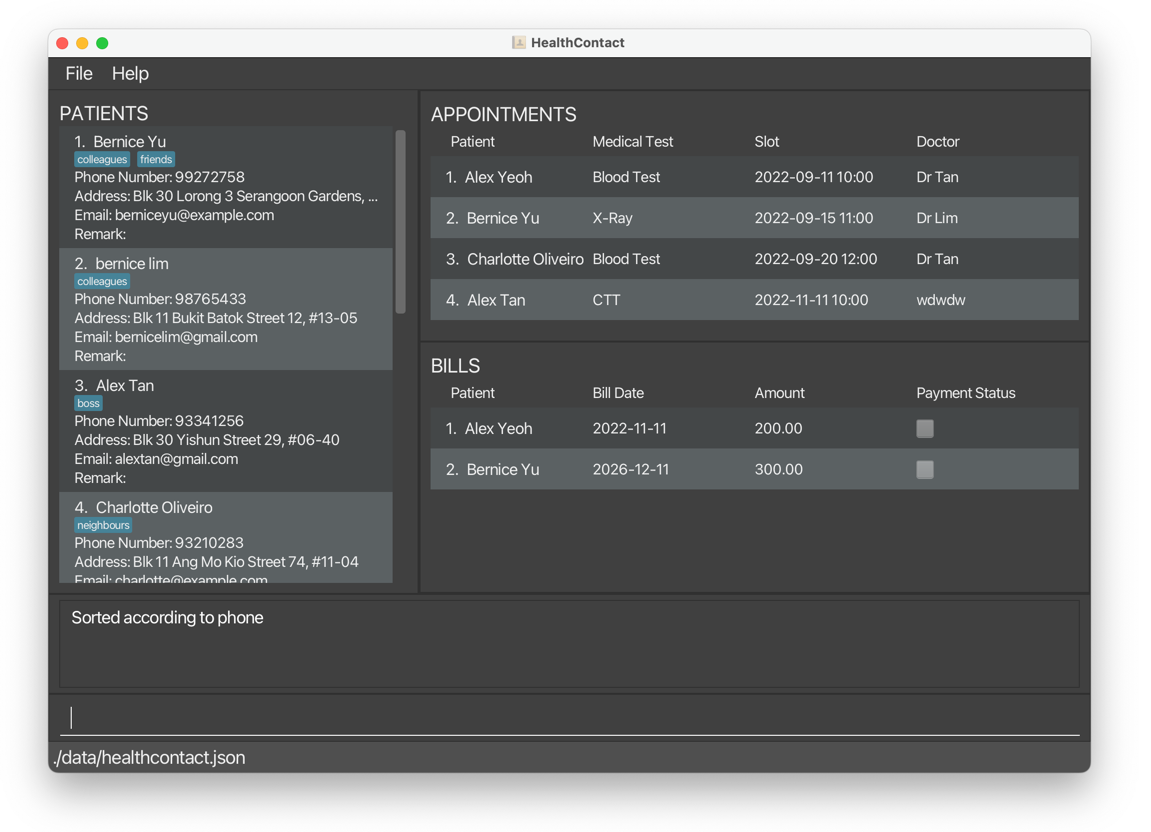
sortpatient c/phone o/descreturns patients sorted by phone number in descending order.
1.4.2 Sort appointments sortappointment, soa
Sorts appointments by a single field.
Command word:
sortappointment or soa
Format:
Command word c/<input> o/<input> ...
- The command word is
sortappointmentorsoa. - The prefixes are
c/for Criteria ando/for Order. - The criteria can be Name of patient (
name), Medical Test of appointment (test), Slot of appointment (slot) and Doctor of appointment (doctor). - The order can be Ascending (
asc) or Descending (desc). - If there are no prefixes keyed in, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the input after a prefix is empty/invalid, an error message with the constraint of the field will be shown.
Examples:
sortappointment c/test o/ascreturns appointments sorted by medical test in ascending order.
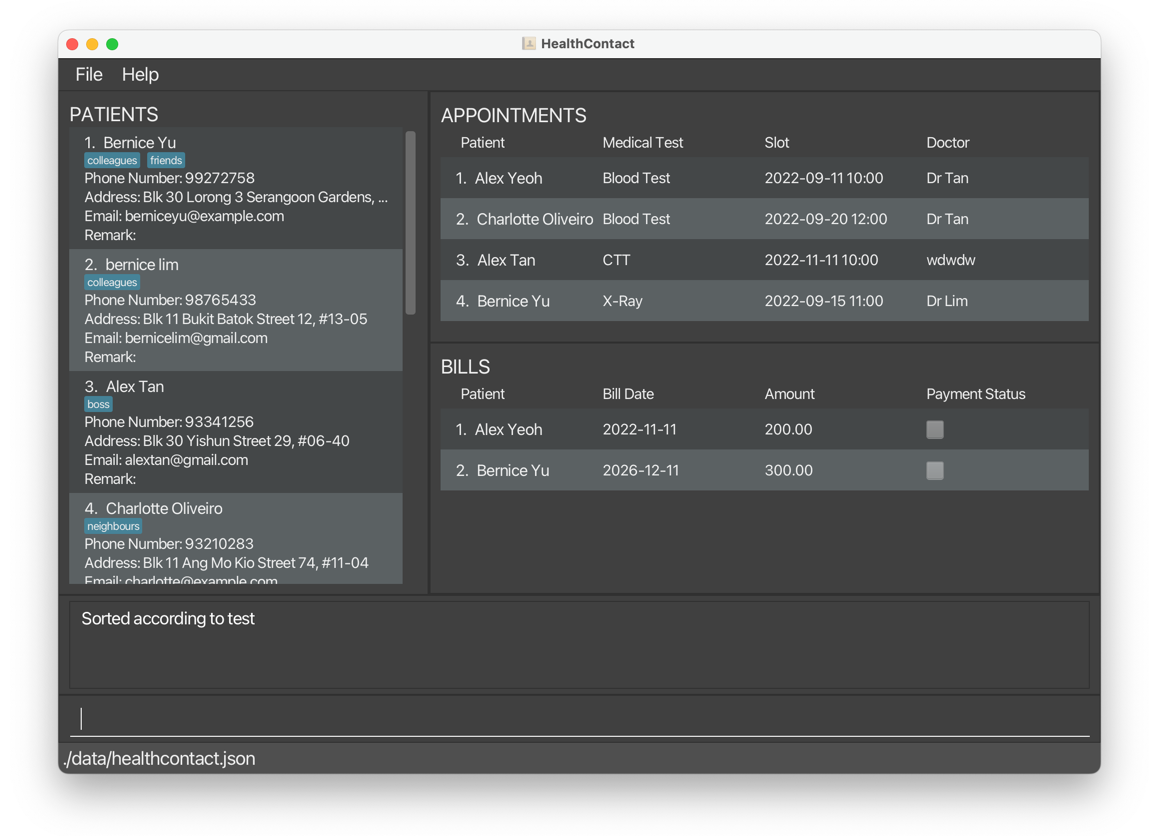
sortappointment c/doctor o/descreturns appointments sorted by doctor in descending order.
1.4.3 Sort bills sortbill, sob
Sorts bills by a single field.
Command word:
sortbill or sob
Format:
Command word c/<input> o/<input> ...
- The command word is
sortbillorsob. - The prefixes are
c/for Criteria ando/for Order. - The criteria can be Name of patient (
name), Amount (amount), Bill date (date), Payment status (status). - The order can be Ascending (
asc) or Descending (desc). - If there are no prefixes keyed in, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the input after a prefix is empty/invalid, an error message with the constraint of the field will be shown.
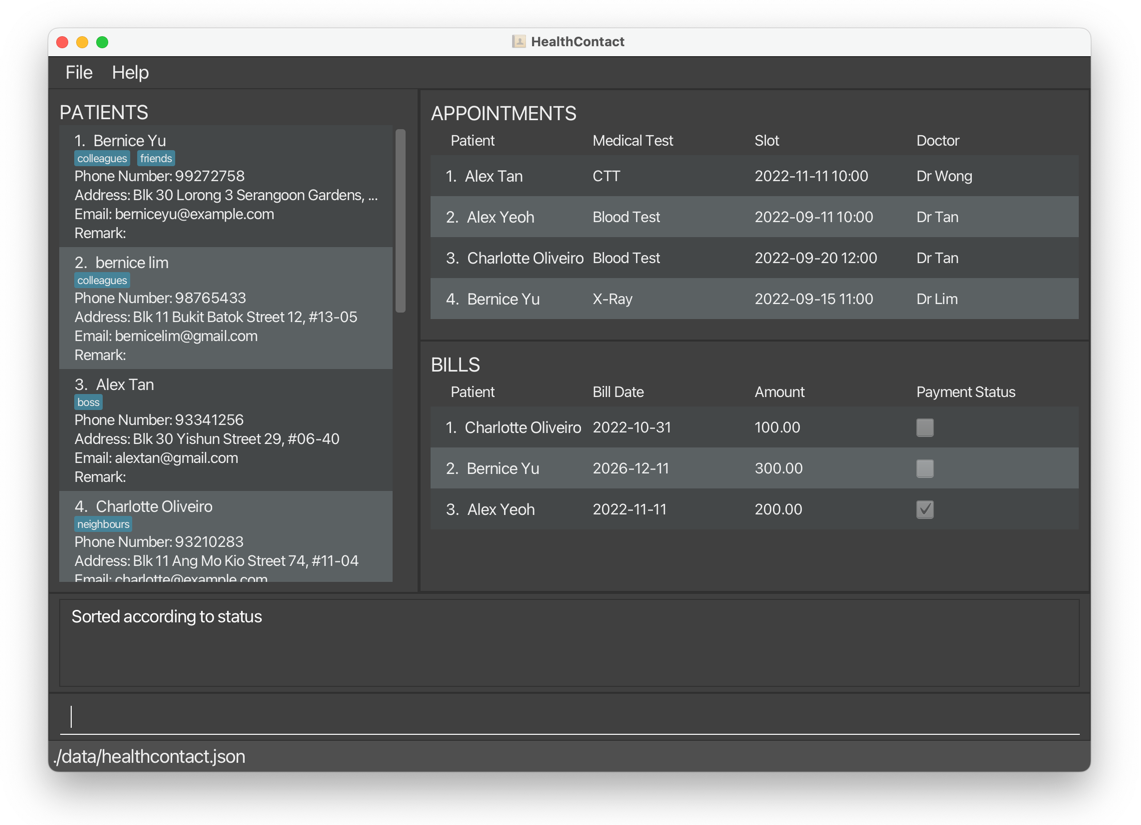
- If the criteria is payment status, Ascending will show bills which are paid first and Descending will show bills which are unpaid first.
Examples:
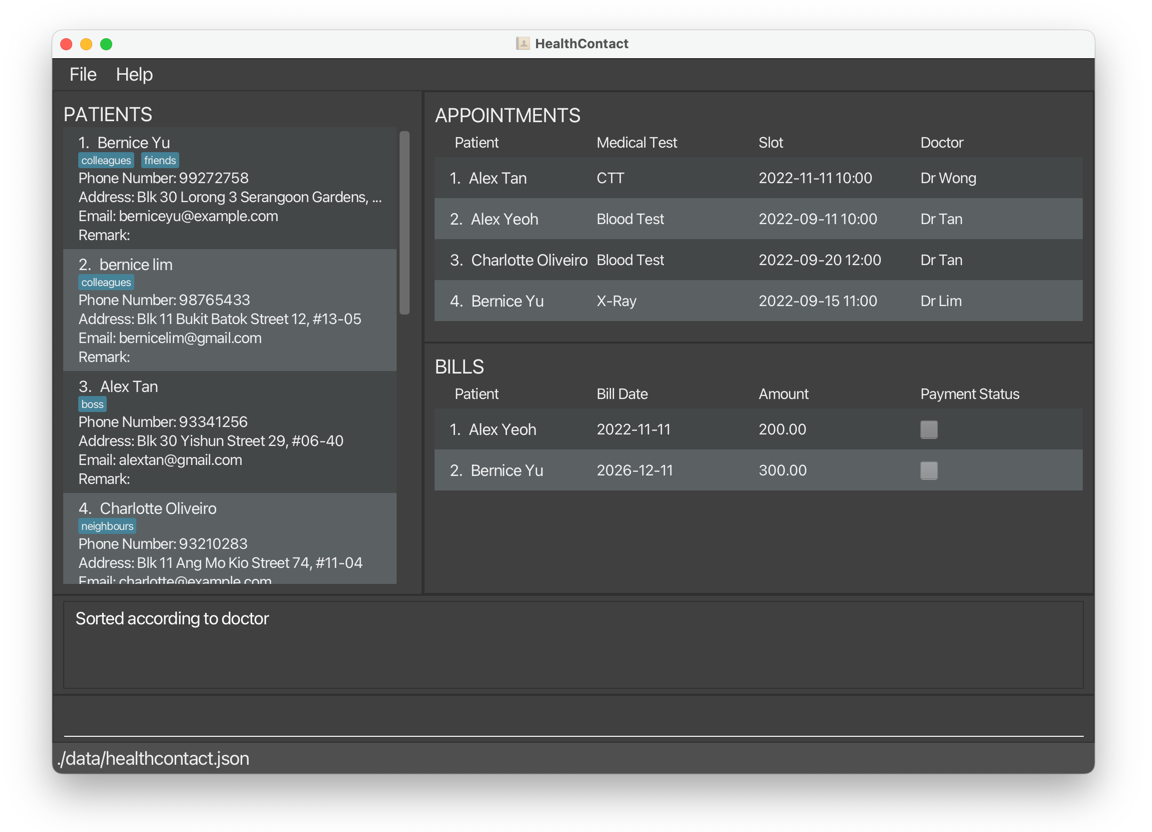
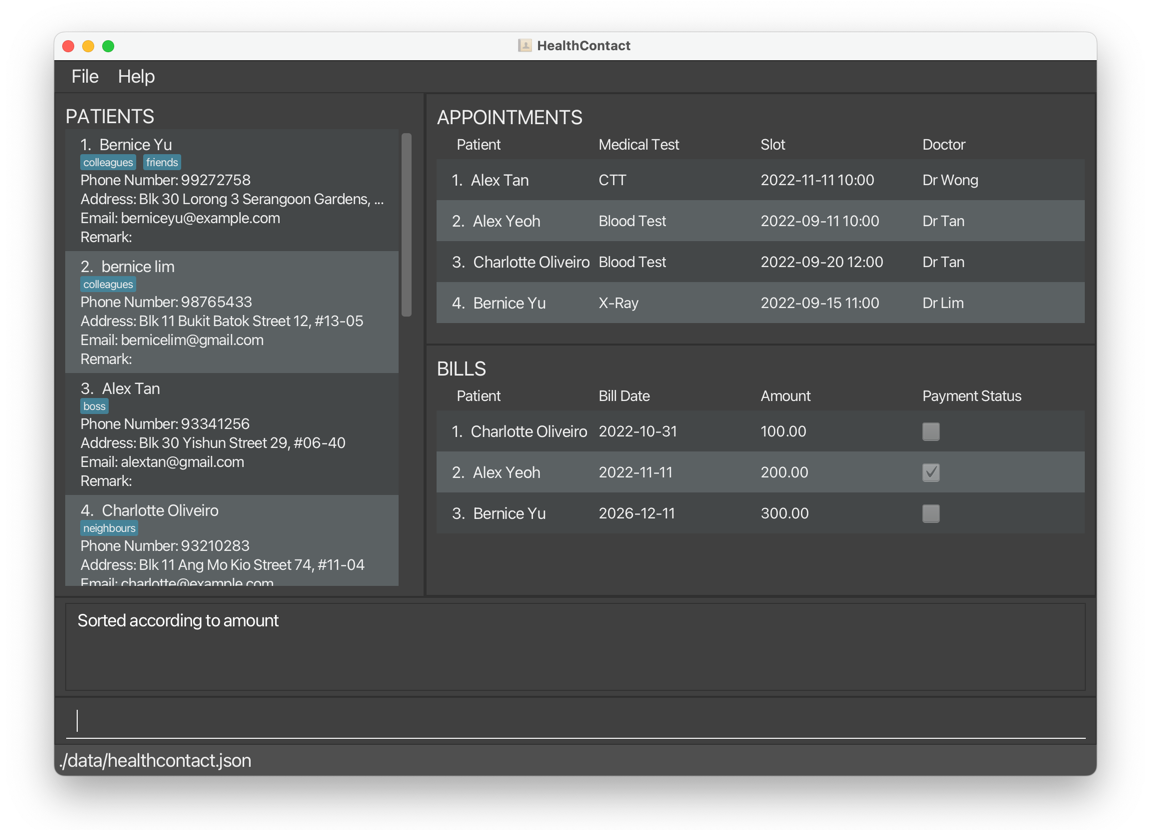
sortbill c/amount o/ascreturns bills sorted by amount in ascending order.
sortbill c/status o/descreturns bills sorted by payment status in descending order.
1.5 Select
Select is a type of command that quickly shows the related information of an item, simulating a mouse click on the item.
1.5.1 Select a patient selectpatient, slp
Selects a patient by index in the patient list. Filter the appointment list and bill list so that these two lists shows the appointments and bills for the selected patient only.
Command word
selectpatient or slp
Format
Command word <index of patient>
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
** |
NA | Index of patient | 1. Positive integer 2. Appears in the patient list |
Notes on symbols in first column:
** Must be directly after command word
Example:
slp 1shows the appointments and bills for the first patient on the patient list.
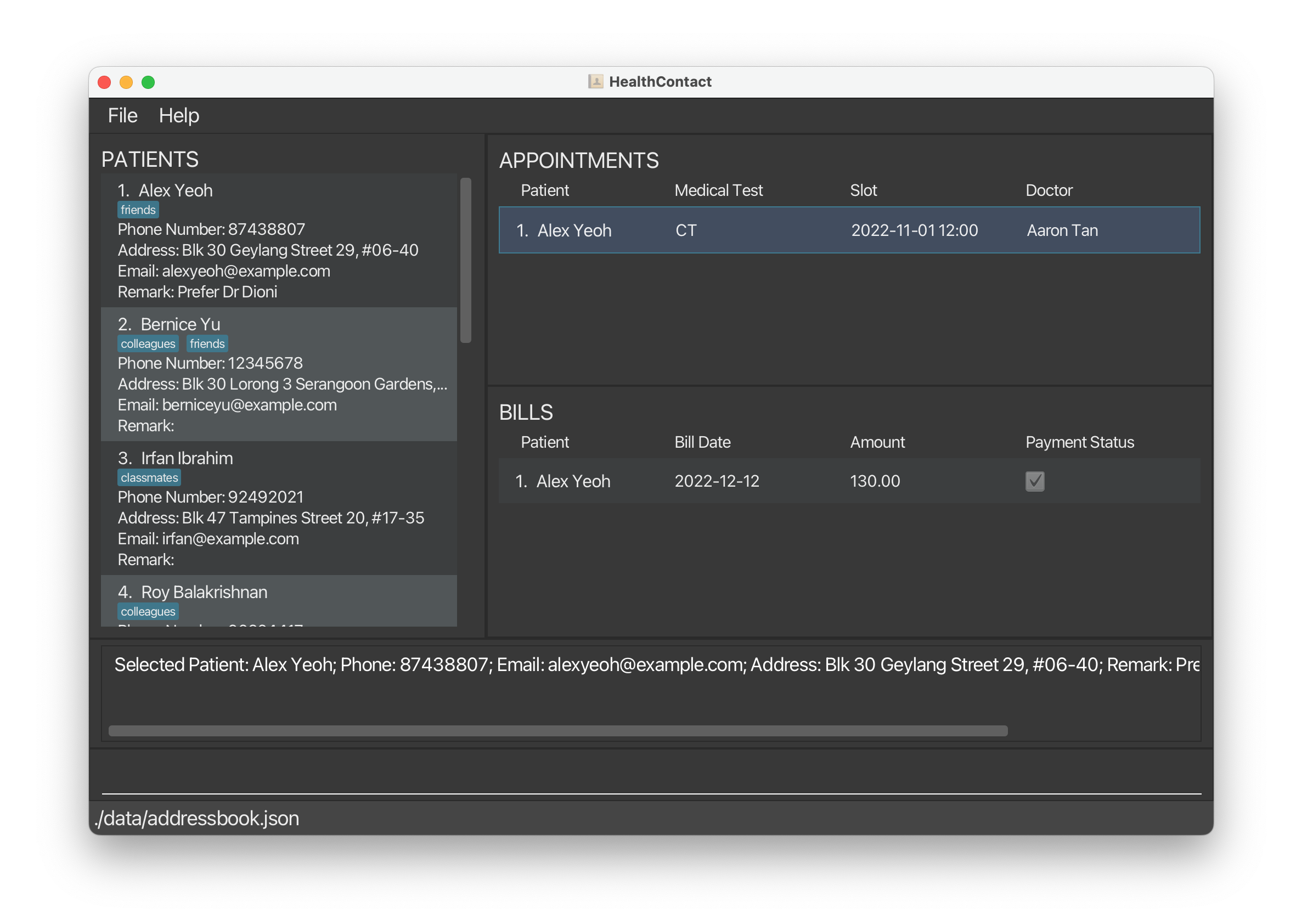
1.5.2 Select an appointment selectappointment, sla
Selects an appointment by index in the appointment list. Filter the bill list so that bill list shows the bill for the selected appointment only.
Command word
selectappointment or sla
Format
Command word <index of appointment>
Parameter List
| Prefix | Meaning | Input Constraint | |
|---|---|---|---|
** |
NA | Index of appointment | 1. Positive integer 2. Appears in the appointment list |
Notes on symbols in first column:
** Must be directly after command word
Example:
sla 1shows the bill for the first appointment on the appointment list.
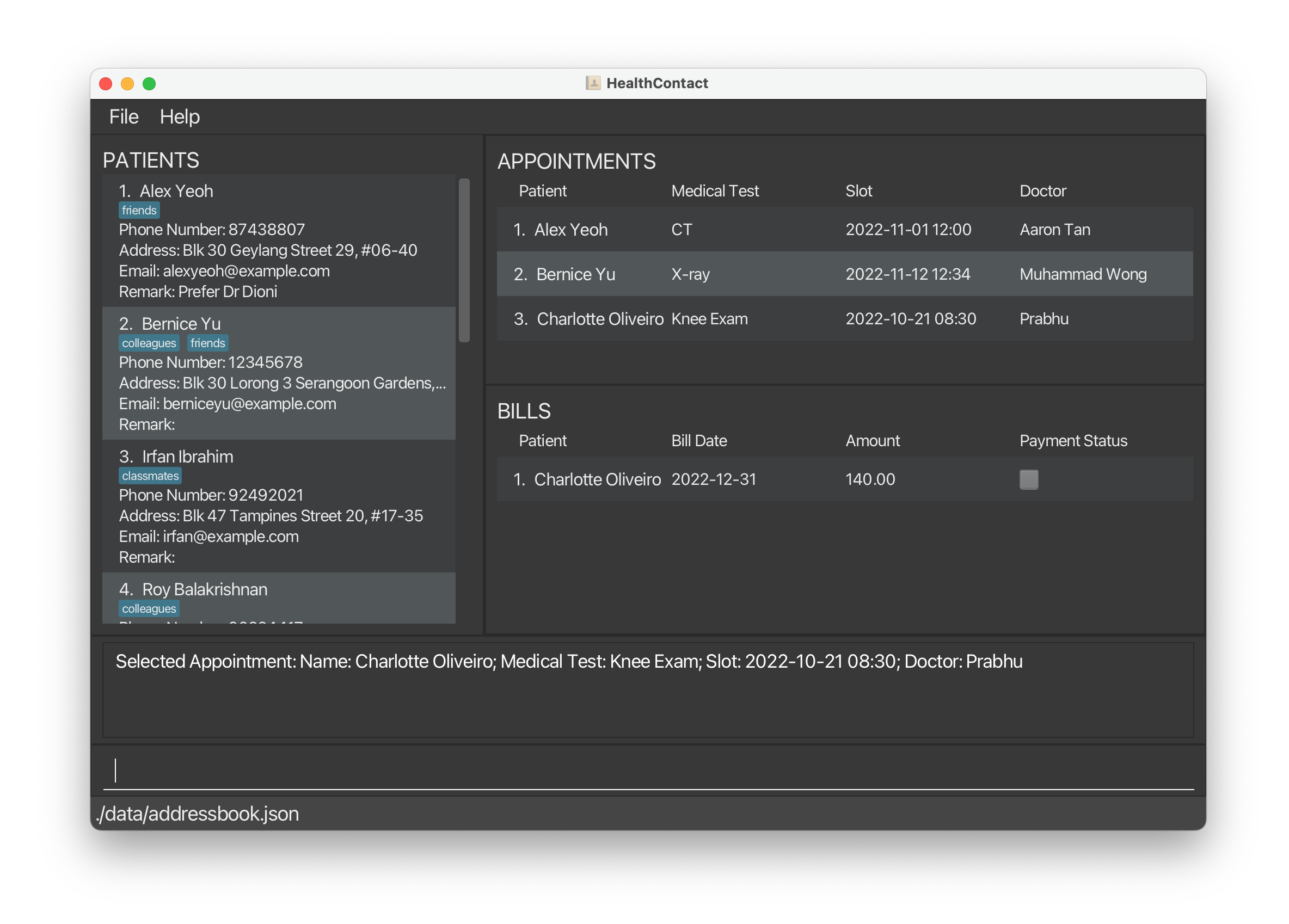
1.6 Set Bill Payment Status
1.6.1 Set Bill As Paid setpaid, sp
Sets the payment status of a bill to “paid”.
Command word:
setpaid or sp
Format:
Command word <index of bill>
- The command words are
setpaidorsp. - The index refers to the index number of the bill shown in the displayed bill list.
- The index must be a valid positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Example:
setpaid 1sets the first bill on the displayed bill list as paid, in this case,Bernice Yu’s bill.
Before:
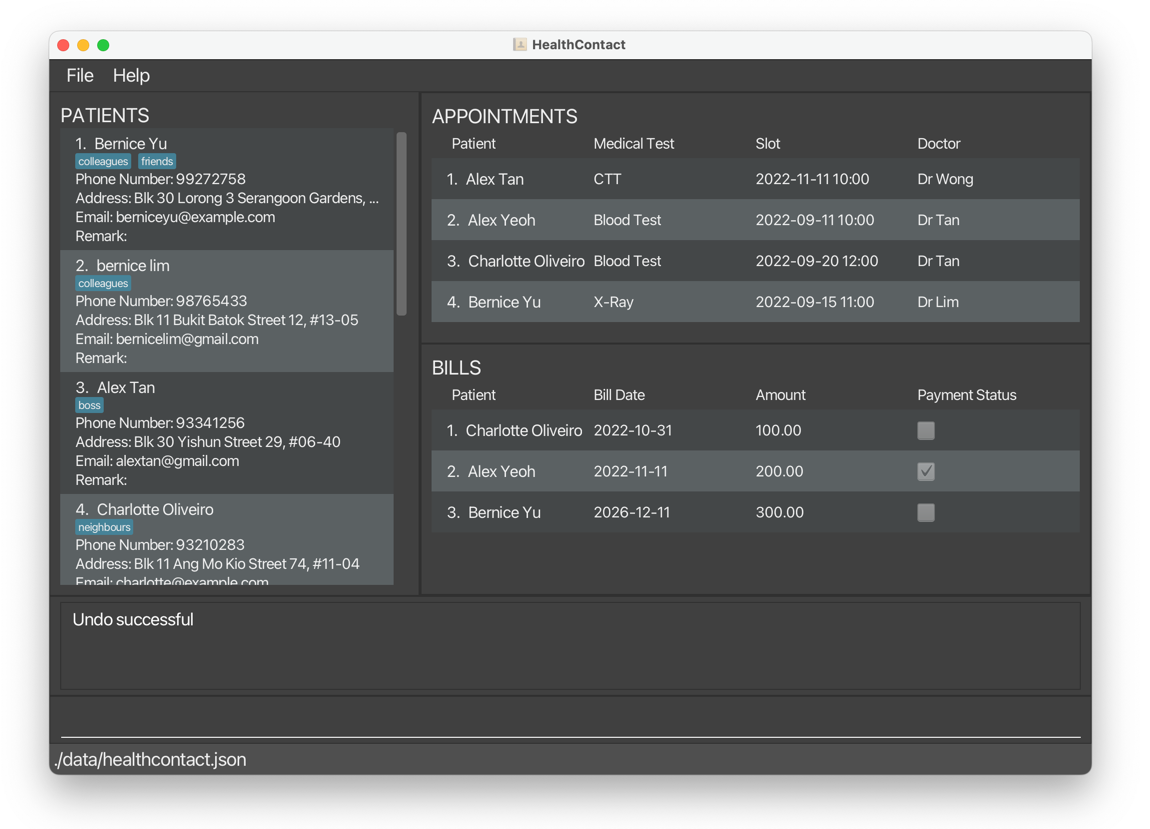
After:
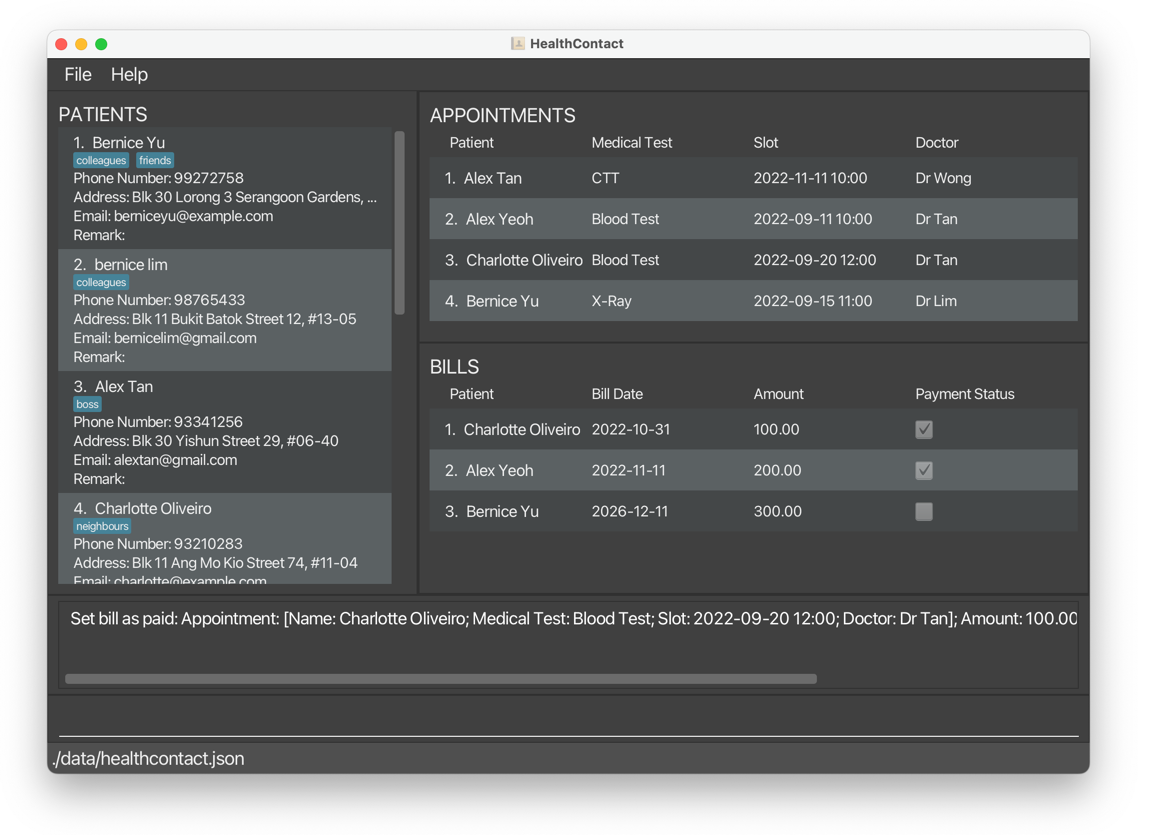
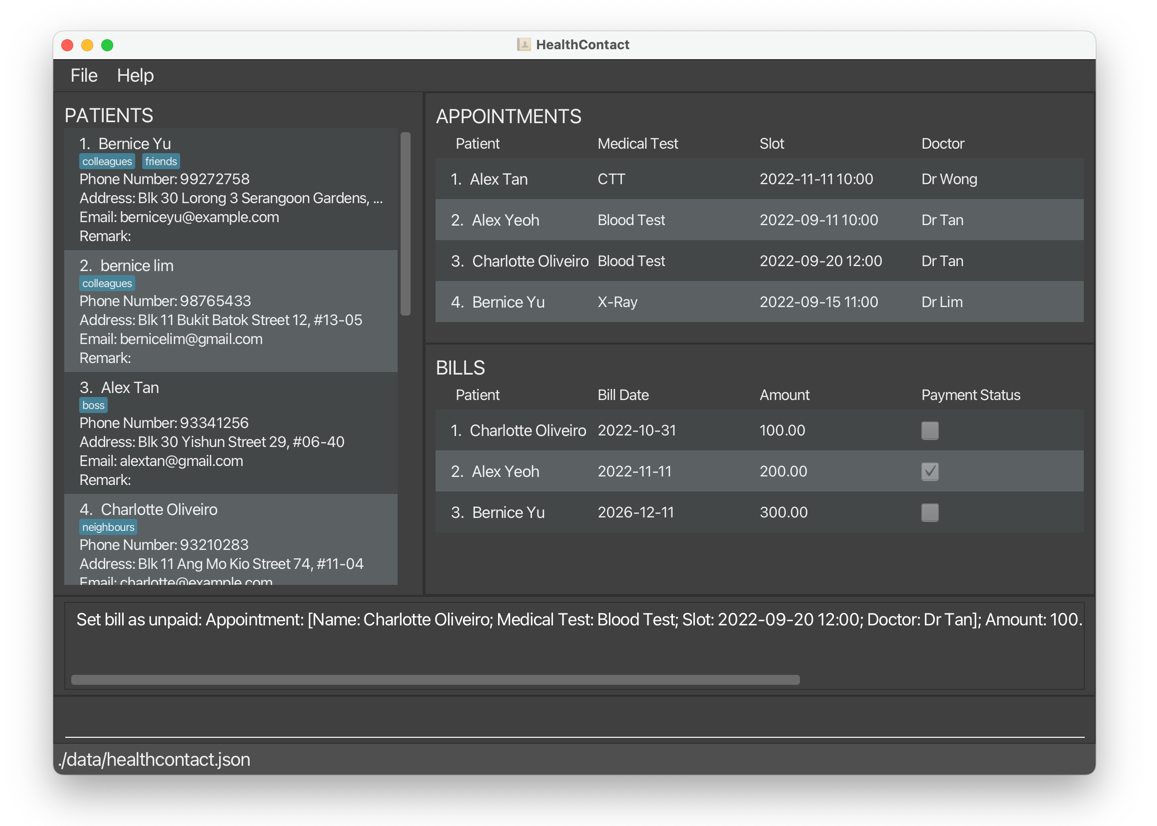
1.6.2 Set Bill As Unpaid setunpaid, sup
Sets the payment status of a bill to “unpaid”.
Command word:
setunpaid or sup
Format:
Command word <index of bill>
- The command words are
setunpaidorsup. - The index refers to the index number of the bill shown in the displayed bill list.
- The index must be a valid positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Example:
setunpaid 1sets the first bill in the displayed bill list as unpaid, in this case,Bernice Yu’s bill.
Before:
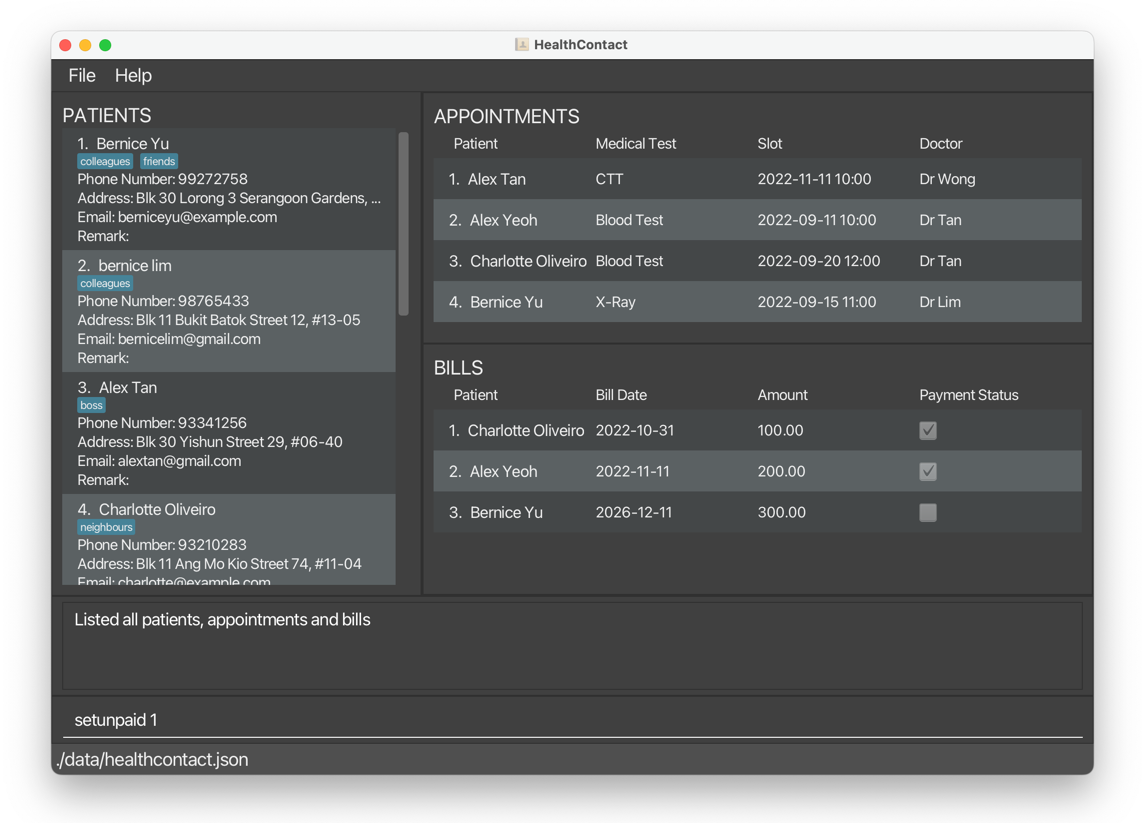
After:
1.7 List list, ls
Removes all conditions previously applied to the list and shows all patients, appointments and bills.
Command word:
list or ls
Format
Command word
Example:
listshows all patients, appointments and bills.
1.8 Delete
1.8.1 Delete a patient deletepatient, dp
Deletes a patient by the index number of the patient in the list.
Command word:
deletepatient or dp
Format:
Command word <index of patient>
- The command words are
deletepatientordp. - The patient to be deleted is identified by using the index in the displayed list.
- Deleting a patient deletes their related appointments and bills.
- If there is no index keyed in or the command word is followed by non-numeric characters, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the index provided is negative or greater than the number of patients in the list, an error message will be shown saying the index is invalid.
Examples:
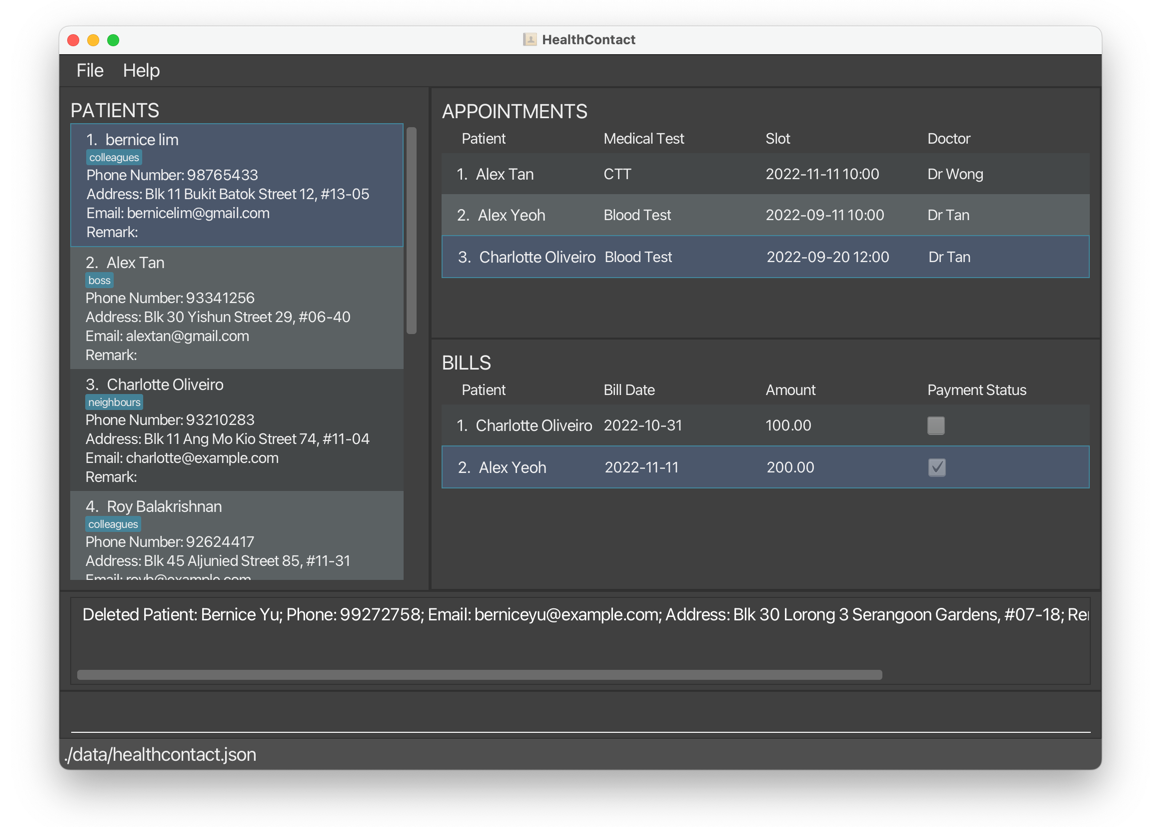
deletepatient 1deletes patientBernice Yuand all of her related appointments and bills.
Before:
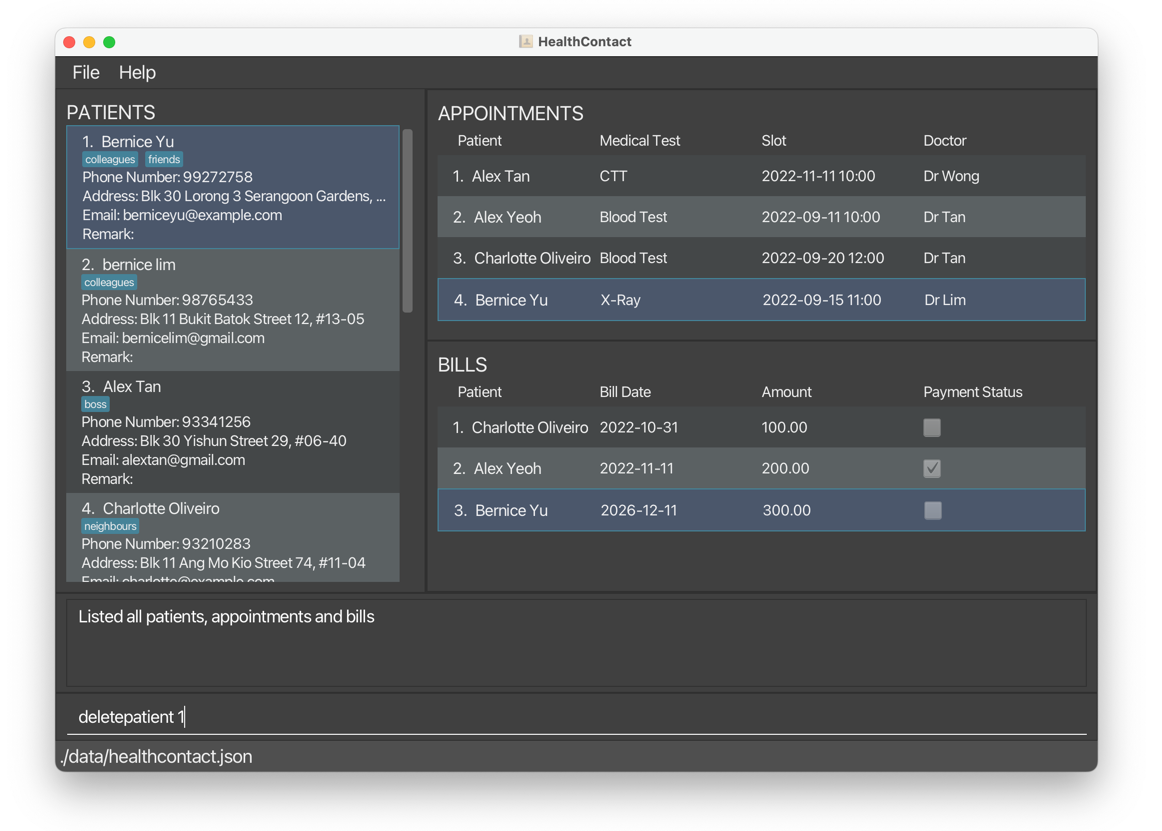
After:
1.8.2 Delete a patient’s appointment deleteappointment, da
Deletes an appointment by the index number of the appointment in the list.
Command word:
deleteappointment or da
Format:
Command word <index of appointment>
- The command words are
deleteappointmentorda. - The appointment to be deleted is identified by using the index in the displayed list.
- Deleting an appointment deletes its related bill.
- If there is no index keyed in or the command word is followed by non-numeric characters, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the index provided is negative or greater than the number of patients in the list, an error message will be shown saying the index is invalid.
Examples:
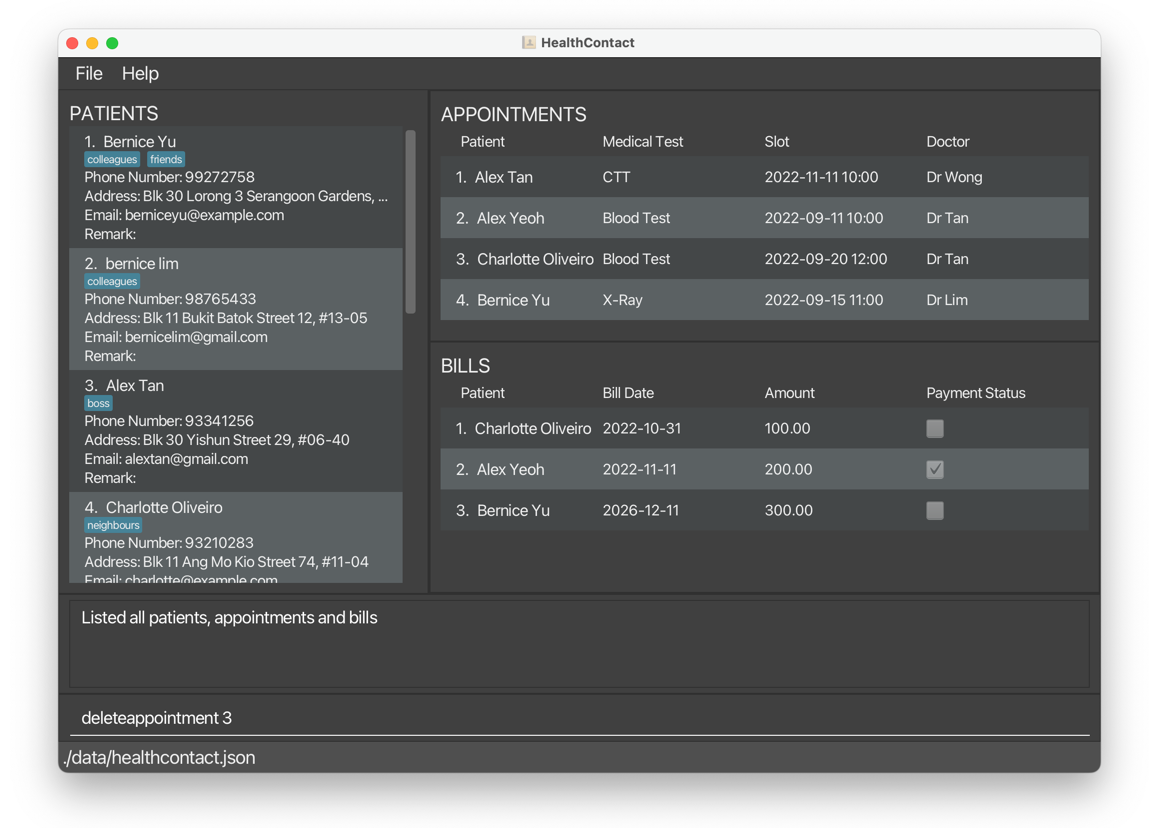
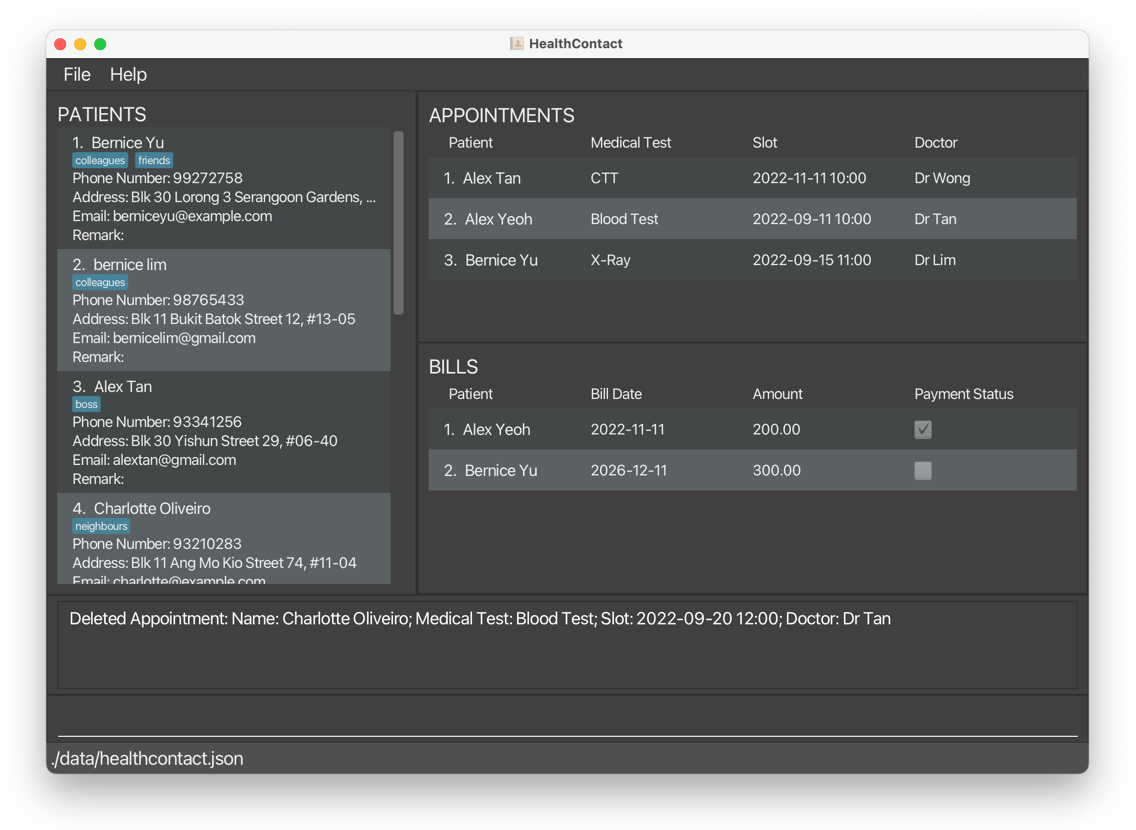
deleteappointment 3deletesCharlotte Oliveiro’s appointment and the bill tagged to it.
Before:
After:
1.8.3 Delete the bill of an appointment deletebill, db
Deletes a bill by the index number of the bill in the list.
Command word:
deletebill or db
Format:
Command word <index of bill>
- The command words are
deletebillordb. - The bill to be deleted is identified by using the index in the displayed list.
- If there is no index keyed in or the command word is followed by non-numeric characters, an error message will be shown with the correct command format.
- If the index provided is negative or greater than the number of patients in the list, an error message will be shown saying the index is invalid.
- The appointment should be deleted only once the bill for the appointment is paid.
Examples:
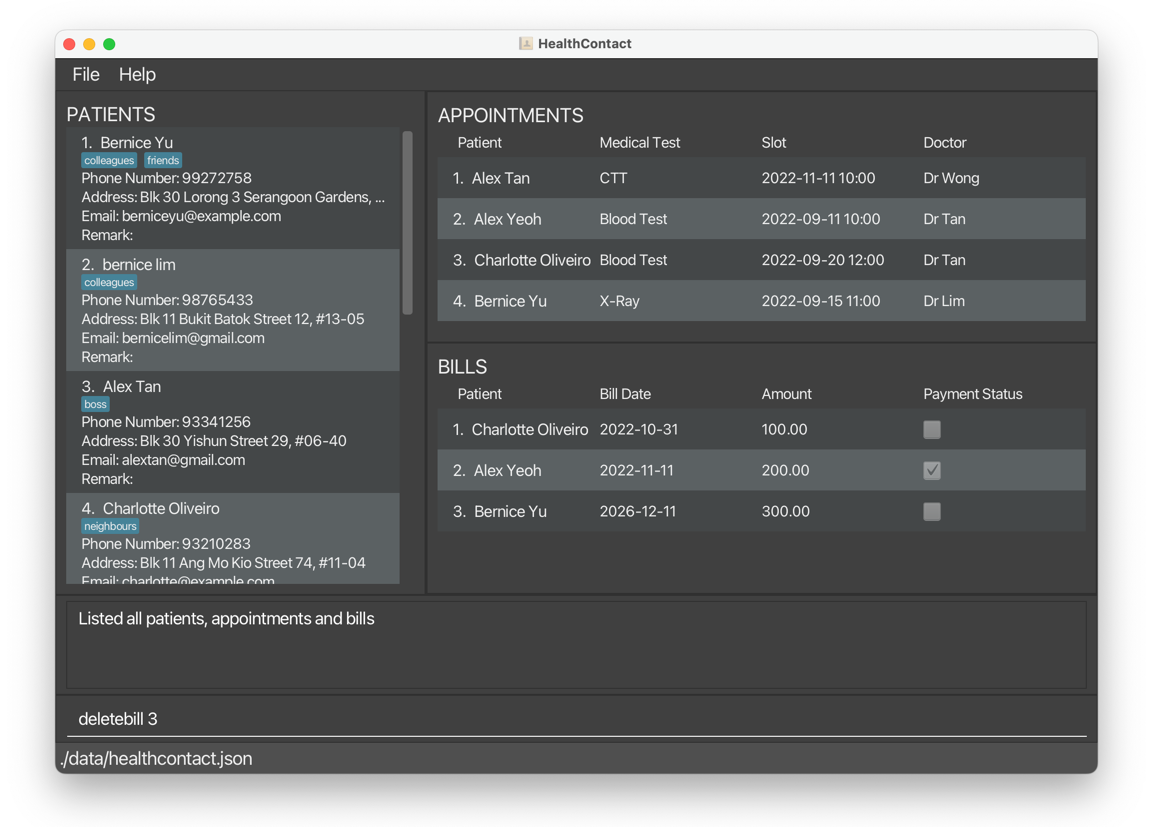
deletebill 3deletesBernice Yu’s bill for herX-Rayappointment.
Before:
After:
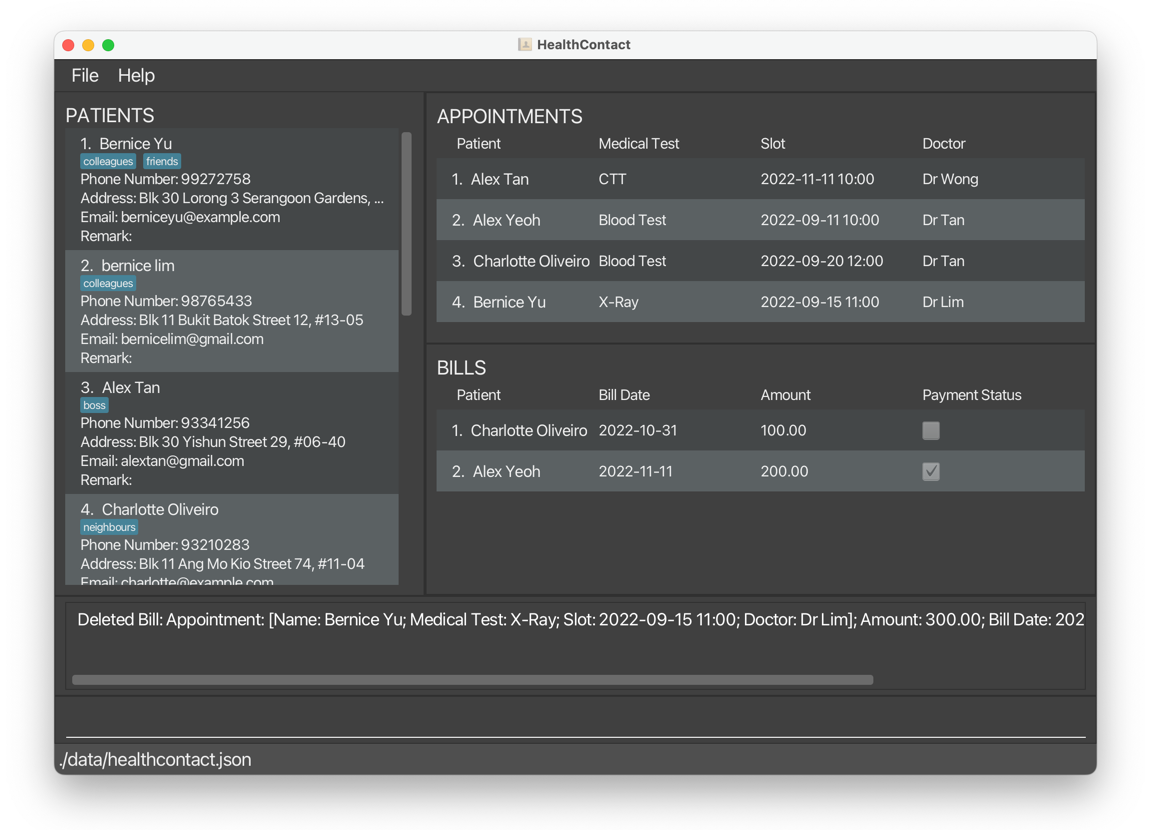
1.9 Undo undo
Reverses the most recent command.
Format:
undo
- The command word is
undo. - The command can be used multiple times to undo multiple commands.
- If there are no commands to undo, an error message will be shown.
- Only commands that change the state of HealthContact can be undone. (Commands such as list, find, select cannot be undone)
Examples:
deletepatient 1deletes all information ofBernice Yu.
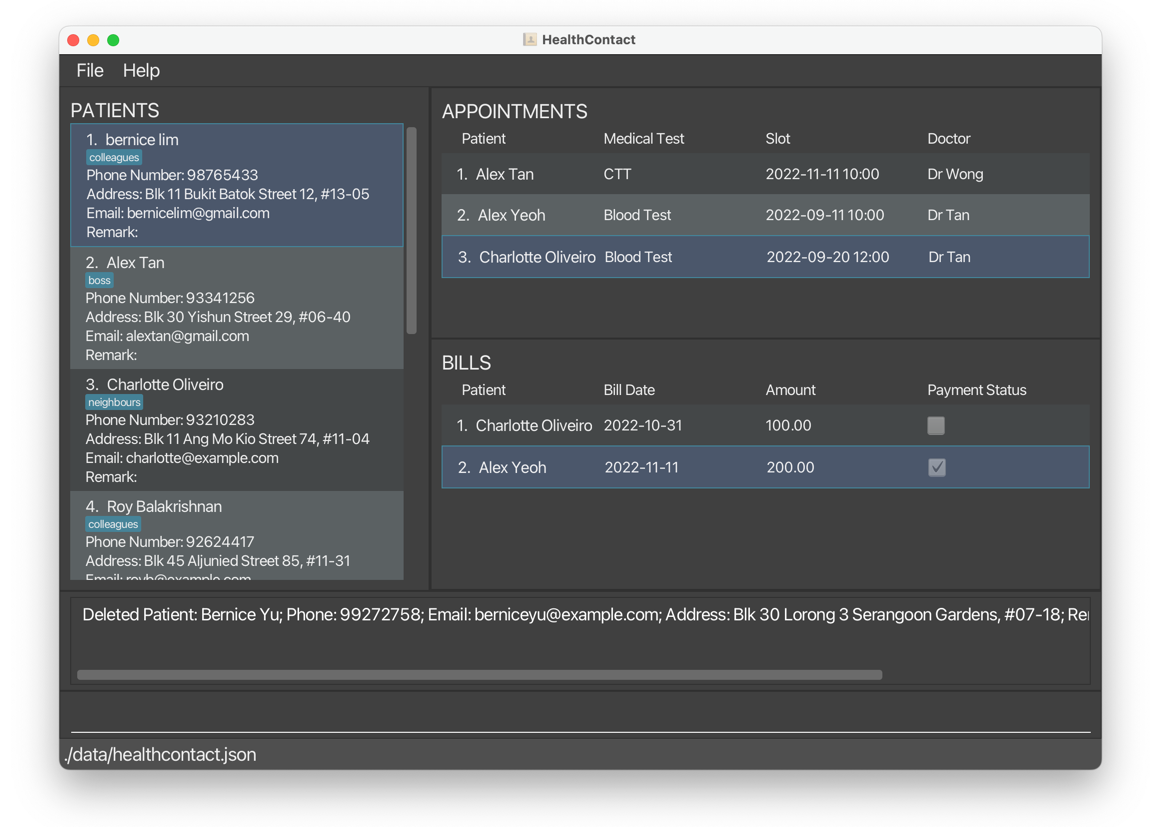
undobrings back all the information ofBernice Yu.
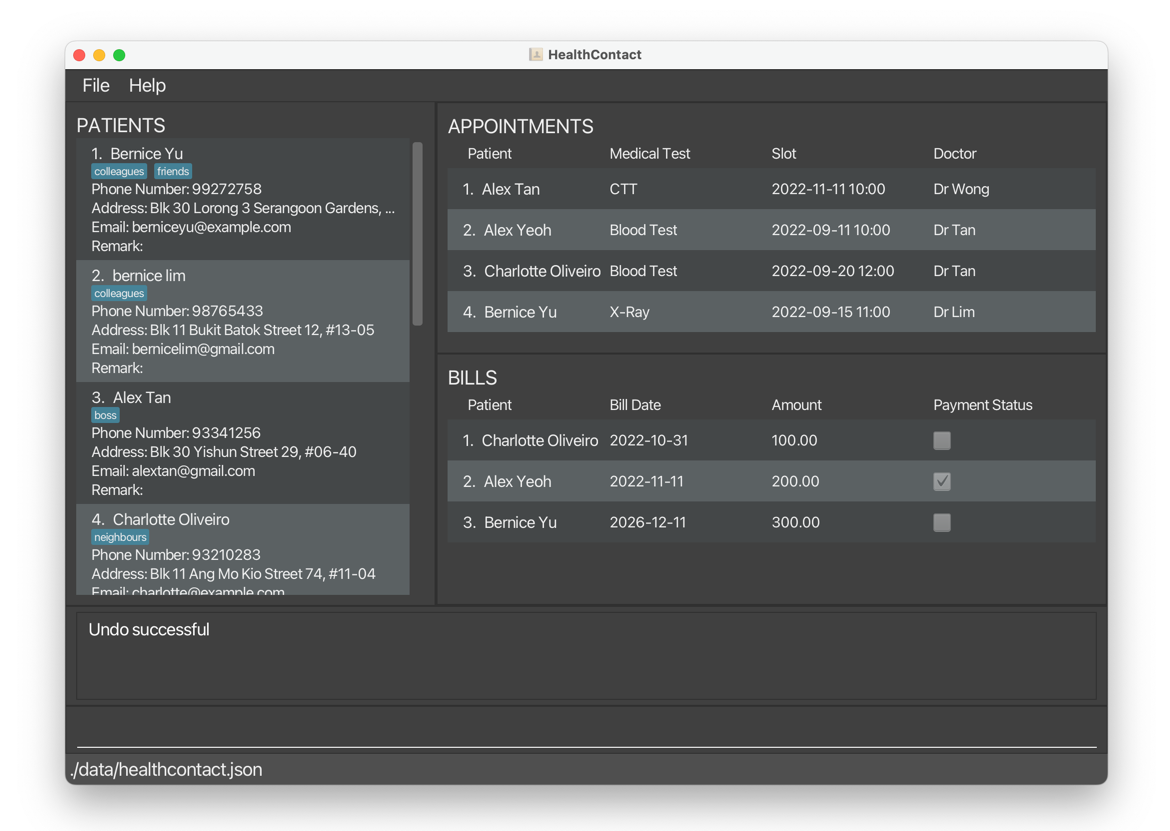
1.10 Redo redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
Format:
redo
- The command word is
redo. - The command can be used multiple times to redo multiple commands.
- If there are no commands to redo, an error message will be shown.
- Executing any command other than undo/redo will clear the redo stack. (i.e. Redo will not work after executing any command other than undo/redo)
Examples:
deletepatient 1deletes all information ofBernice Yu.
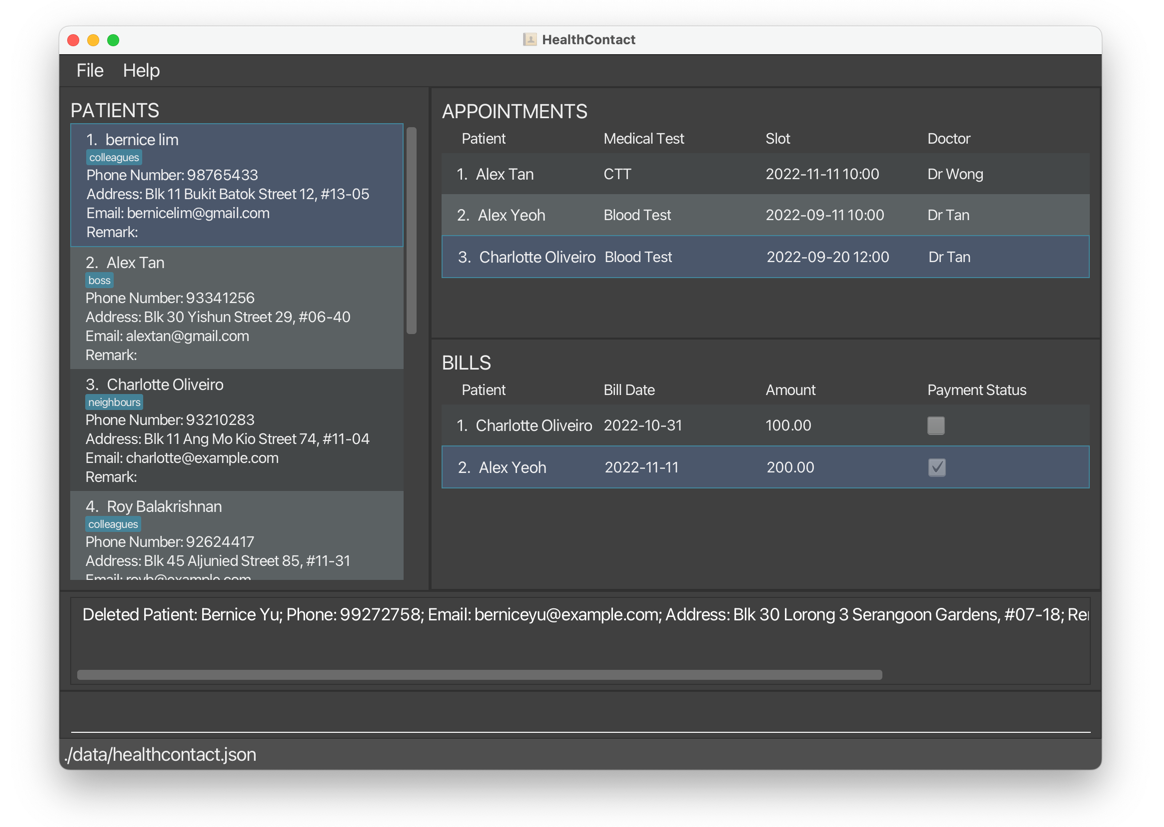
undobrings back all information ofBernice Yu.
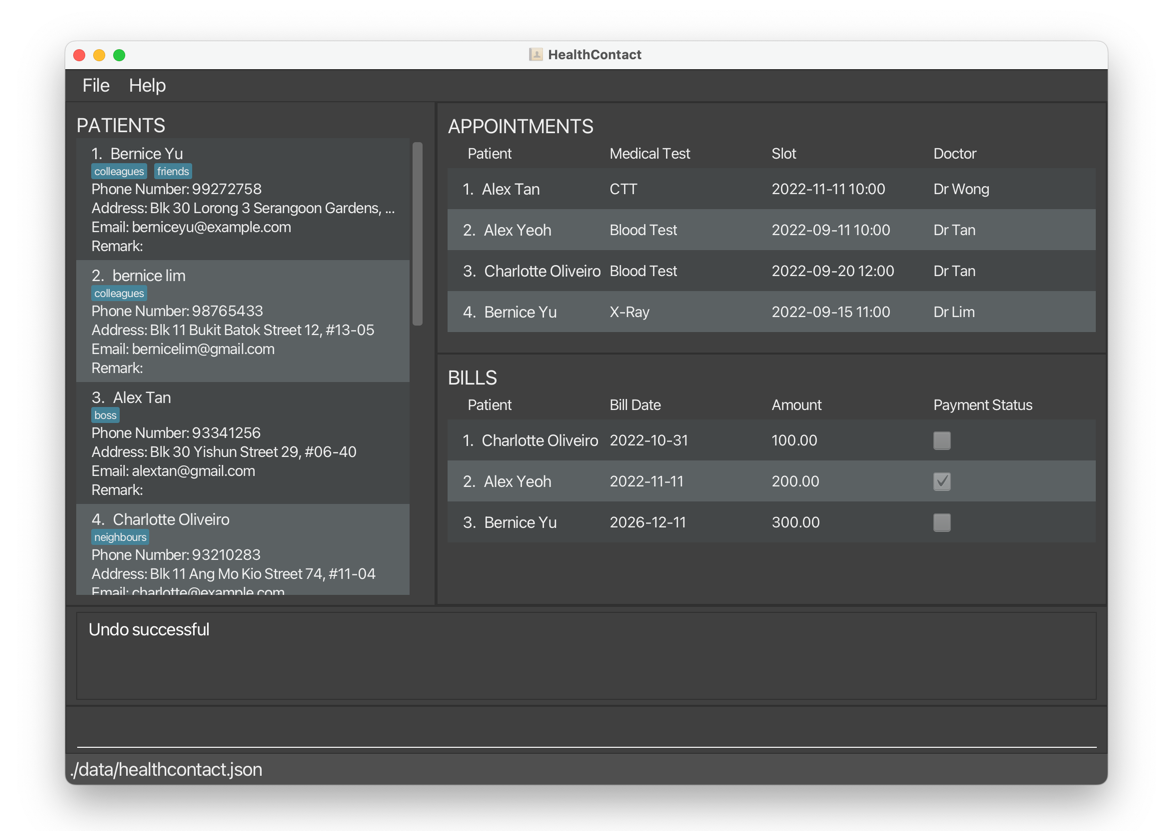
redodeletes all information ofBernice Yuagain.
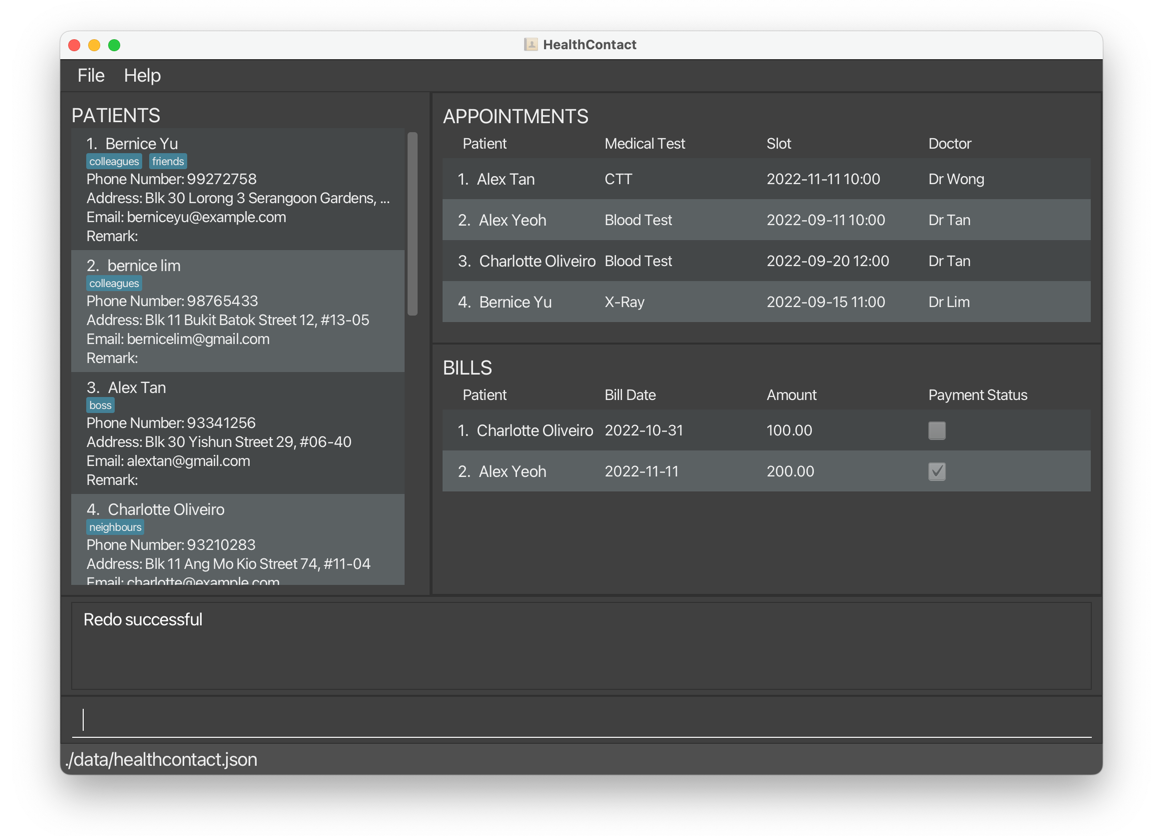
1.11 Clear clear
Deletes all patients, appointments and bills from HealthContact.
- If the user accidentally clears all data, the user can restore the data by using the
undocommand. If the user closes the application before undoingclear, the data will be gone permanently.
Format
clear
Example
cleardeletes all the data in HealthContact.
1.12 Exit exit
Quits HealthContact.
Format
exit
Example
- Executing
exit, the program closes.
1.13 Help help
Opens the Help Window.
Format
help
Example
helpopens the help window.
1.14 Save the data
HealthContact data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
1.15 Edit the data file
HealthContact data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/healthcontact.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
- If the changes to the data file makes its format invalid, HealthContact will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run.
2. Command Summary Table
| Feature | Command Word | Shortcut | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Add | a patient | addpatient |
ap |
| an appointment of a patient | addappointment |
aa |
|
| a bill for an appointment | addbill |
ab |
|
| Edit | a patient | editpatient |
ep |
| an appointment of a patient | editappointment |
ea |
|
| a bill for an appointment | editbill |
eb |
|
| Delete | a patient | deletepatient |
dp |
| an appointment of a patient | deleteappointment |
da |
|
| a bill for an appointment | deletebill |
db |
|
| Find | a patient | findpatient |
fp |
| an appointment of a patient | findappointment |
fa |
|
| a bill for an appointment | findbill |
fb |
|
| Sort | patients | sortpatient |
sop |
| appointments | sortappointment |
soa |
|
| bills | sortbill |
sob |
|
| Select | a patient | selectpatient |
slp |
| an appointment | selectappointment |
sla |
|
| Set bill | as paid | setpaid |
sp |
| as unpaid | setunpaid |
sup |
|
| Undo | the last change | undo |
|
| Redo | the last undone change | redo |
|
| Clear | all the data saved | clear |
|
| List | all patients, appointments and bills | list |
ls |
| Exit | the program | exit |
|
| Help | the user with user guide | help |
3. Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: How do I find out which appointment a bill is for?
- Use the FindAppointmentCommand to find all appointments for a patient using the patient name on the bill. Then, use the SelectAppointmentCommand to see which appointment is the bill for.
- Q: What do I do if I cannot open the application by double-clicking on it?
- Try opening the application by running the command
java -jar HealthContact.jarin the command prompt.
- Try opening the application by running the command
- Q: What do I do if the data on the application panels are too long and are partially hidden by “…”?
- Use select commands to view the details or expand the application window.